Filter
Associated Lab
- Aso Lab (1) Apply Aso Lab filter
- Betzig Lab (113) Apply Betzig Lab filter
- Bock Lab (1) Apply Bock Lab filter
- Clapham Lab (2) Apply Clapham Lab filter
- Fetter Lab (2) Apply Fetter Lab filter
- Harris Lab (7) Apply Harris Lab filter
- Hess Lab (8) Apply Hess Lab filter
- Ji Lab (11) Apply Ji Lab filter
- Lavis Lab (8) Apply Lavis Lab filter
- Lippincott-Schwartz Lab (6) Apply Lippincott-Schwartz Lab filter
- Liu (Zhe) Lab (7) Apply Liu (Zhe) Lab filter
- Magee Lab (2) Apply Magee Lab filter
- Rubin Lab (1) Apply Rubin Lab filter
- Saalfeld Lab (2) Apply Saalfeld Lab filter
- Schreiter Lab (1) Apply Schreiter Lab filter
- Shroff Lab (9) Apply Shroff Lab filter
- Singer Lab (1) Apply Singer Lab filter
- Svoboda Lab (2) Apply Svoboda Lab filter
- Tjian Lab (4) Apply Tjian Lab filter
- Turner Lab (1) Apply Turner Lab filter
Associated Project Team
Publication Date
- 2025 (2) Apply 2025 filter
- 2024 (2) Apply 2024 filter
- 2023 (4) Apply 2023 filter
- 2022 (3) Apply 2022 filter
- 2021 (2) Apply 2021 filter
- 2020 (4) Apply 2020 filter
- 2019 (7) Apply 2019 filter
- 2018 (6) Apply 2018 filter
- 2017 (8) Apply 2017 filter
- 2016 (12) Apply 2016 filter
- 2015 (11) Apply 2015 filter
- 2014 (8) Apply 2014 filter
- 2013 (4) Apply 2013 filter
- 2012 (5) Apply 2012 filter
- 2011 (7) Apply 2011 filter
- 2010 (3) Apply 2010 filter
- 2009 (2) Apply 2009 filter
- 2008 (8) Apply 2008 filter
- 2007 (2) Apply 2007 filter
- 2006 (1) Apply 2006 filter
- 2005 (1) Apply 2005 filter
- 1995 (1) Apply 1995 filter
- 1994 (2) Apply 1994 filter
- 1993 (2) Apply 1993 filter
- 1992 (4) Apply 1992 filter
- 1991 (2) Apply 1991 filter
Type of Publication
113 Publications
Showing 101-110 of 113 resultsWe introduce a method for optically imaging intracellular proteins at nanometer spatial resolution. Numerous sparse subsets of photoactivatable fluorescent protein molecules were activated, localized (to approximately 2 to 25 nanometers), and then bleached. The aggregate position information from all subsets was then assembled into a superresolution image. We used this method–termed photoactivated localization microscopy–to image specific target proteins in thin sections of lysosomes and mitochondria; in fixed whole cells, we imaged vinculin at focal adhesions, actin within a lamellipodium, and the distribution of the retroviral protein Gag at the plasma membrane.
Commentary: The original PALM paper by myself and my friend and co-inventor Harald Hess, spanning the before- and after-HHMI eras. Submitted and publicly presented months before other publications in the same year, the lessons of the paper remain widely misunderstood: 1) localization precision is not resolution; 2) the ability to resolve a few molecules by the Rayleigh criterion in a diffraction limited region (DLR) does not imply the ability to resolve structures of arbitrary complexity at the same scale; 3) true resolution well beyond the Abbe limit requires the ability to isolate and localize hundreds or thousands of molecules in one DLR; and 4) certain photoactivatable fluorescent proteins (PA-FPs) and caged dyes can be isolated and precisely localized at such densities; yielding true resolution down to 20 nm. The molecular densities we demonstrate (105 molecules/m2) are more than two orders of magnitude greater than in later papers that year (implying ten-fold better true resolution) – indeed, these papers demonstrate densities only comparable to earlier spectral or photobleaching based isolation methods. We validate our claims by correlative electron microscopy, and demonstrate the outstanding advantages of PA-FPs for superresolution microscopy: minimally perturbative sample preparation; high labeling densities; close binding to molecular targets; and zero non-specific background.
A method is described that yields a series of (D+1)-element wave-vector sets giving rise to (D=2 or 3)-dimensional coherent sparse lattices of any desired Bravais symmetry and primitive cell shape, but of increasing period relative to the excitation wavelength. By applying lattice symmetry operations to any of these sets, composite lattices of N>D+1 waves are constructed, having increased spatial frequency content but unchanged crystal group symmetry and periodicity. Optical lattices of widely spaced excitation maxima of diffraction-limited confinement and controllable polarization can thereby be created, possibly useful for quan- tum optics, lithography, or multifocal microscopy.
Commentary: Develops a formalism to find a set of wavevectors that create a periodic optical lattice of any desired Bravais symmetry by the mutual interference of the corresponding plane waves. Discovers two new classes of optical lattices, sparse and composite, that together permit the creation of widely spaced, tightly confined excitation maxima in 3D potentially suitable for high speed volumetric live cell imaging. The implementation of this idea was derailed by our exclusive focus on PALM at the time, and many of its goals have since been reached with our Bessel beam plane illumination microscope. Nevertheless, sparse and composite optical lattices may prove useful in atomic physics or for the fabrication of 3D nanostructures.
We can resolve multiple discrete features within a focal region of m spatial dimensions by first isolating each on the basis of n >/= 1 unique optical characteristics and then measuring their relative spatial coordinates. The minimum acceptable separation between features depends on the point-spread function in the (m + n)d-dimensional space formed by the spatial coordinates and the optical parameters, whereas the absolute spatial resolution is determined by the accuracy to which the coordinates can be measured. Estimates of each suggest that near-field fluorescence excitation microscopy/spectroscopy with molecular sensitivity and spatial resolution is possible.
Commentary: Inspired by my earlier work (see below) in single molecule imaging and the isolation of multiple exciton recombination sites within a single probe volume, here I proposed the principle which would eventually lead to PALM. Indeed, all methods of localization microscopy, including PALM, fPALM, PALMIRA, STORM, dSTORM, PAINT, GSDIM, etc. are specific embodiments of the general principle of single molecule isolation and localization I introduced here.
Luminescent centers with sharp (<0.07 millielectron volt), spectrally distinct emission lines were imaged in a GaAs/AIGaAs quantum well by means of low-temperature near-field scanning optical microscopy. Temperature, magnetic field, and linewidth measurements establish that these centers arise from excitons laterally localized at interface fluctuations. For sufficiently narrow wells, virtually all emission originates from such centers. Near-field microscopy/spectroscopy provides a means to access energies and homogeneous line widths for the individual eigenstates of these centers, and thus opens a rich area of physics involving quantum resolved systems.
Luminescent centers with sharp (<0.07 millielectron volt), spectrally distinct emission lines were imaged in a GaAs/AIGaAs quantum well by means of low-temperature near-field scanning optical microscopy. Temperature, magnetic field, and linewidth measurements establish that these centers arise from excitons laterally localized at interface fluctuations. For sufficiently narrow wells, virtually all emission originates from such centers. Near-field microscopy/spectroscopy provides a means to access energies and homogeneous line widths for the individual eigenstates of these centers, and thus opens a rich area of physics involving quantum resolved systems.
Commentary: Harald Hess and I joined forces, combining my near-field optical technology with his cryogenic scanned probe microscope to produce the first paper on high resolution spectroscopy beyond the diffraction limit. We discovered that the broad luminescence spectrum traditionally observed from quantum well heterostructures reflects a resolution-limited ensemble average of emission from numerous discrete sites of exciton recombination occurring at atomic-scale corrugations in the confining interfaces. With the combination of high spatial resolution from near-field excitation and high spectral resolution from cryogenic operation, we were able to isolate these emission sites in a multidimensional space of xy position and wavelength, even though their density was too great to isolate them on the basis of spatial resolution alone. This insight was very influential in the genesis of the concept (see above) that would eventually lead to far-field superresolution by PALM.
Individual carbocyanine dye molecules in a sub-monolayer spread have been imaged with near-field scanning optical microscopy. Molecules can be repeatedly detected and spatially localized (to approximately lambda/50 where lambda is the wavelength of light) with a sensitivity of at least 0.005 molecules/(Hz)(1/2) and the orientation of each molecular dipole can be determined. This information is exploited to map the electric field distribution in the near-field aperture with molecular spatial resolution.
Commentary: A paper of many firsts: the first single molecule microscopy; the first extended observations of single molecules under ambient conditions; the first localization of single molecules to near-molecular precision ( 15 nm), the first determination of the dipole axes of single fluorescent molecules; and the first near-molecular resolution optical microscopy, when a single fluorescent molecule was used to map the evanescent electric field components in the vicinity of a 100 nm diameter near-field aperture. Although eventually supplanted by simpler far-field methods, this paper ushered in the era of single molecule imaging and biophysics, and inspired the concept that would eventually lead to PALM. Even today, near-field single molecule detection lives on in the “zero mode waveguide” sequencing approach promoted by Pacific Biosciences.
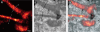
Near-field scanning optical microscopy (NSOM) has been used to generate high resolution flourescence images of cytoskeletal actin within fixed mouse fibroblast cells. Comparison with other microscopic methods indicates a transverse resolution well beyond that of confocal microscopy, and contrast far more revealing than in force microscopy. Effects unique to the near field are shown to be involved in the excitation of flourescence, yet the resulting images remain readily interpretable. As an initial demonstration of its utility, the technique is used to analyze the actin-based cytoskeletal structure between stress fibers and in cellular protrusions formed in the process of wound healing.
Commentary: The first superresolution fluorescence imaging of a biological system: the actin cytoskeleton in fixed, cultured fibroblast cells. This work strongly influenced me in two ways. First, calculations based on the signal-to-noise-ratio in images of single actin filaments in the paper suggested that single molecule imaging might be feasible. This was soon proven to be the case (see above). Second, the limitations of exogenous labeling for superresolution microscopy were revealed: samples which appeared correctly stained by conventional microscopy often exhibited sketchy, punctuate labeling of actin filaments as well as substantial non-specific background in the corresponding near field images. Indeed, it was the advent of GFP, with its promise of dense labeling and perfect specificity, that lured me back to superresolution microscopy when I first heard of it in 2003.
Recent advances in probe design have led to enhanced resolution (currently as significant as 12 nm) in optical microscopes based on near-field imaging. We demonstrate that the polarization of emitted and detected light in such microscopes can be manipulated sensitively to generate contrast. We show that the contrast on certain patterns is consistent with a simple interpretation of the requisite boundary conditions, whereas in other cases a more complicated interaction between the probe and the sample is involved. Finally application of the technique to near-filed magneto-optic imaging is demonstrated.
The near-field optical interaction between a sharp probe and a sample of interest can be exploited to image, spectroscopically probe, or modify surfaces at a resolution (down to approximately 12 nm) inaccessible by traditional far-field techniques. Many of the attractive features of conventional optics are retained, including noninvasiveness, reliability, and low cost. In addition, most optical contrast mechanisms can be extended to the near-field regime, resulting in a technique of considerable versatility. This versatility is demonstrated by several examples, such as the imaging of nanometric-scale features in mammalian tissue sections and the creation of ultrasmall, magneto-optic domains having implications for highdensity data storage. Although the technique may find uses in many diverse fields, two of the most exciting possibilities are localized optical spectroscopy of semiconductors and the fluorescence imaging of living cells.
Commentary: An overview of our work in near-field optics at the time, after our invention of the adiabatically tapered fiber probe and shear force feedback (see below) led to the first practical near-field scanning optical microscope. In this work, superresolution imaging via absorption, reflectivity, fluorescence, spectroscopy, polarization, and refractive index contrast were all demonstrated. Unlike all far-field superresolution fluorescence methods that were to appear a decade later, near-field microscopy remains the only superresolution technique capable of taking advantage of the full panoply of optical contrast mechanisms.
A distance regulation method has been developed to enhance the reliability, versatility, and ease of use of near-field scanning optical microscopy (NSOM). The method relies on the detection of shear forces between the end of a near-field probe and the sample of interest. The system can be used solely for distance regulation in NSOM, for simultaneous shear force and near-field imaging, or for shear force microscopy alone. In the latter case, uncoated optical fiber probes are found to yield images with consistently high resolution.
Commentary: To exploit the evanescent field that is the source of high resolution in near-field microscopy, the probe must be exceptionally close to the sample: 10 nm away for 30-50 nm resolution. Here we introduced a distance regulation mechanism based on transverse shear forces between the end of a dithered near-field probe and the sample, which permitted even samples of modest topography to be imaged. Simple, reliable, noninvasive, and applicable to a wide range of samples from whole fixed cells to semiconductor devices, shear force microscopy was a key enabling technology for near-field optics, and soon widely implemented.