Filter
Associated Lab
- Aguilera Castrejon Lab (15) Apply Aguilera Castrejon Lab filter
- Ahrens Lab (56) Apply Ahrens Lab filter
- Aso Lab (39) Apply Aso Lab filter
- Baker Lab (38) Apply Baker Lab filter
- Betzig Lab (110) Apply Betzig Lab filter
- Beyene Lab (10) Apply Beyene Lab filter
- Bock Lab (17) Apply Bock Lab filter
- Branson Lab (48) Apply Branson Lab filter
- Card Lab (40) Apply Card Lab filter
- Cardona Lab (63) Apply Cardona Lab filter
- Chklovskii Lab (13) Apply Chklovskii Lab filter
- Clapham Lab (12) Apply Clapham Lab filter
- Cui Lab (19) Apply Cui Lab filter
- Darshan Lab (12) Apply Darshan Lab filter
- Dennis Lab (1) Apply Dennis Lab filter
- Dickson Lab (46) Apply Dickson Lab filter
- Druckmann Lab (25) Apply Druckmann Lab filter
- Dudman Lab (46) Apply Dudman Lab filter
- Eddy/Rivas Lab (30) Apply Eddy/Rivas Lab filter
- Egnor Lab (11) Apply Egnor Lab filter
- Espinosa Medina Lab (16) Apply Espinosa Medina Lab filter
- Feliciano Lab (6) Apply Feliciano Lab filter
- Fetter Lab (41) Apply Fetter Lab filter
- Fitzgerald Lab (28) Apply Fitzgerald Lab filter
- Freeman Lab (15) Apply Freeman Lab filter
- Funke Lab (34) Apply Funke Lab filter
- Gonen Lab (91) Apply Gonen Lab filter
- Grigorieff Lab (62) Apply Grigorieff Lab filter
- Harris Lab (58) Apply Harris Lab filter
- Heberlein Lab (94) Apply Heberlein Lab filter
- Hermundstad Lab (22) Apply Hermundstad Lab filter
- Hess Lab (71) Apply Hess Lab filter
- Ilanges Lab (1) Apply Ilanges Lab filter
- Jayaraman Lab (44) Apply Jayaraman Lab filter
- Ji Lab (33) Apply Ji Lab filter
- Johnson Lab (6) Apply Johnson Lab filter
- Kainmueller Lab (19) Apply Kainmueller Lab filter
- Karpova Lab (14) Apply Karpova Lab filter
- Keleman Lab (13) Apply Keleman Lab filter
- Keller Lab (75) Apply Keller Lab filter
- Koay Lab (16) Apply Koay Lab filter
- Lavis Lab (136) Apply Lavis Lab filter
- Lee (Albert) Lab (34) Apply Lee (Albert) Lab filter
- Leonardo Lab (23) Apply Leonardo Lab filter
- Li Lab (25) Apply Li Lab filter
- Lippincott-Schwartz Lab (161) Apply Lippincott-Schwartz Lab filter
- Liu (Yin) Lab (5) Apply Liu (Yin) Lab filter
- Liu (Zhe) Lab (58) Apply Liu (Zhe) Lab filter
- Looger Lab (137) Apply Looger Lab filter
- Magee Lab (49) Apply Magee Lab filter
- Menon Lab (18) Apply Menon Lab filter
- Murphy Lab (13) Apply Murphy Lab filter
- O'Shea Lab (4) Apply O'Shea Lab filter
- Otopalik Lab (13) Apply Otopalik Lab filter
- Pachitariu Lab (41) Apply Pachitariu Lab filter
- Pastalkova Lab (18) Apply Pastalkova Lab filter
- Pavlopoulos Lab (19) Apply Pavlopoulos Lab filter
- Pedram Lab (14) Apply Pedram Lab filter
- Podgorski Lab (16) Apply Podgorski Lab filter
- Reiser Lab (49) Apply Reiser Lab filter
- Riddiford Lab (44) Apply Riddiford Lab filter
- Romani Lab (40) Apply Romani Lab filter
- Rubin Lab (139) Apply Rubin Lab filter
- Saalfeld Lab (60) Apply Saalfeld Lab filter
- Satou Lab (16) Apply Satou Lab filter
- Scheffer Lab (36) Apply Scheffer Lab filter
- Schreiter Lab (62) Apply Schreiter Lab filter
- Sgro Lab (20) Apply Sgro Lab filter
- Shroff Lab (23) Apply Shroff Lab filter
- Simpson Lab (23) Apply Simpson Lab filter
- Singer Lab (80) Apply Singer Lab filter
- Spruston Lab (91) Apply Spruston Lab filter
- Stern Lab (152) Apply Stern Lab filter
- Sternson Lab (54) Apply Sternson Lab filter
- Stringer Lab (29) Apply Stringer Lab filter
- Svoboda Lab (135) Apply Svoboda Lab filter
- Tebo Lab (31) Apply Tebo Lab filter
- Tervo Lab (9) Apply Tervo Lab filter
- Tillberg Lab (17) Apply Tillberg Lab filter
- Tjian Lab (64) Apply Tjian Lab filter
- Truman Lab (88) Apply Truman Lab filter
- Turaga Lab (46) Apply Turaga Lab filter
- Turner Lab (35) Apply Turner Lab filter
- Vale Lab (6) Apply Vale Lab filter
- Voigts Lab (2) Apply Voigts Lab filter
- Wang (Meng) Lab (9) Apply Wang (Meng) Lab filter
- Wang (Shaohe) Lab (24) Apply Wang (Shaohe) Lab filter
- Wu Lab (9) Apply Wu Lab filter
- Zlatic Lab (28) Apply Zlatic Lab filter
- Zuker Lab (25) Apply Zuker Lab filter
Associated Project Team
- CellMap (5) Apply CellMap filter
- COSEM (3) Apply COSEM filter
- Fly Descending Interneuron (10) Apply Fly Descending Interneuron filter
- Fly Functional Connectome (14) Apply Fly Functional Connectome filter
- Fly Olympiad (5) Apply Fly Olympiad filter
- FlyEM (51) Apply FlyEM filter
- FlyLight (46) Apply FlyLight filter
- GENIE (40) Apply GENIE filter
- Integrative Imaging (1) Apply Integrative Imaging filter
- Larval Olympiad (2) Apply Larval Olympiad filter
- MouseLight (16) Apply MouseLight filter
- NeuroSeq (1) Apply NeuroSeq filter
- ThalamoSeq (1) Apply ThalamoSeq filter
- Tool Translation Team (T3) (24) Apply Tool Translation Team (T3) filter
- Transcription Imaging (49) Apply Transcription Imaging filter
Publication Date
- 2024 (141) Apply 2024 filter
- 2023 (175) Apply 2023 filter
- 2022 (192) Apply 2022 filter
- 2021 (193) Apply 2021 filter
- 2020 (196) Apply 2020 filter
- 2019 (202) Apply 2019 filter
- 2018 (232) Apply 2018 filter
- 2017 (217) Apply 2017 filter
- 2016 (209) Apply 2016 filter
- 2015 (252) Apply 2015 filter
- 2014 (236) Apply 2014 filter
- 2013 (194) Apply 2013 filter
- 2012 (190) Apply 2012 filter
- 2011 (190) Apply 2011 filter
- 2010 (161) Apply 2010 filter
- 2009 (158) Apply 2009 filter
- 2008 (140) Apply 2008 filter
- 2007 (106) Apply 2007 filter
- 2006 (92) Apply 2006 filter
- 2005 (67) Apply 2005 filter
- 2004 (57) Apply 2004 filter
- 2003 (58) Apply 2003 filter
- 2002 (39) Apply 2002 filter
- 2001 (28) Apply 2001 filter
- 2000 (29) Apply 2000 filter
- 1999 (14) Apply 1999 filter
- 1998 (18) Apply 1998 filter
- 1997 (16) Apply 1997 filter
- 1996 (10) Apply 1996 filter
- 1995 (18) Apply 1995 filter
- 1994 (12) Apply 1994 filter
- 1993 (10) Apply 1993 filter
- 1992 (6) Apply 1992 filter
- 1991 (11) Apply 1991 filter
- 1990 (11) Apply 1990 filter
- 1989 (6) Apply 1989 filter
- 1988 (1) Apply 1988 filter
- 1987 (7) Apply 1987 filter
- 1986 (4) Apply 1986 filter
- 1985 (5) Apply 1985 filter
- 1984 (2) Apply 1984 filter
- 1983 (2) Apply 1983 filter
- 1982 (3) Apply 1982 filter
- 1981 (3) Apply 1981 filter
- 1980 (1) Apply 1980 filter
- 1979 (1) Apply 1979 filter
- 1976 (2) Apply 1976 filter
- 1973 (1) Apply 1973 filter
- 1970 (1) Apply 1970 filter
- 1967 (1) Apply 1967 filter
Type of Publication
3920 Publications
Showing 2391-2400 of 3920 resultsOxytocin plays a critical role in regulating social behaviors, yet our understanding of its function in both neurological health and disease remains incomplete. Real-time oxytocin imaging probes with spatiotemporal resolution relevant to its endogenous signaling are required to fully elucidate oxytocin's role in the brain. Herein, we describe a near-infrared oxytocin nanosensor (nIROXT), a synthetic probe capable of imaging oxytocin in the brain without interference from its structural analogue, vasopressin. nIROXT leverages the inherent tissue-transparent fluorescence of single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNT) and the molecular recognition capacity of an oxytocin receptor peptide fragment to selectively and reversibly image oxytocin. We employ these nanosensors to monitor electrically stimulated oxytocin release in brain tissue, revealing oxytocin release sites with a median size of 3 µm in the paraventricular nucleus of C57BL/6 mice, which putatively represents the spatial diffusion of oxytocin from its point of release. These data demonstrate that covalent SWCNT constructs, such as nIROXT, are powerful optical tools that can be leveraged to measure neuropeptide release in brain tissue.
Imaging approaches based on single molecule localization break the diffraction barrier of conventional fluorescence microscopy, allowing for bioimaging with nanometer resolution. It remains a challenge, however, to precisely localize photon-limited single molecules in 3D. We have developed a new localization-based imaging technique achieving almost isotropic subdiffraction resolution in 3D. A tilted mirror is used to generate a side view in addition to the front view of activated single emitters, allowing their 3D localization to be precisely determined for superresolution imaging. Because both front and side views are in focus, this method is able to efficiently collect emitted photons. The technique is simple to implement on a commercial fluorescence microscope, and especially suitable for biological samples with photon-limited chromophores such as endogenously expressed photoactivatable fluorescent proteins. Moreover, this method is relatively resistant to optical aberration, as it requires only centroid determination for localization analysis. Here we demonstrate the application of this method to 3D imaging of bacterial protein distribution and neuron dendritic morphology with subdiffraction resolution.
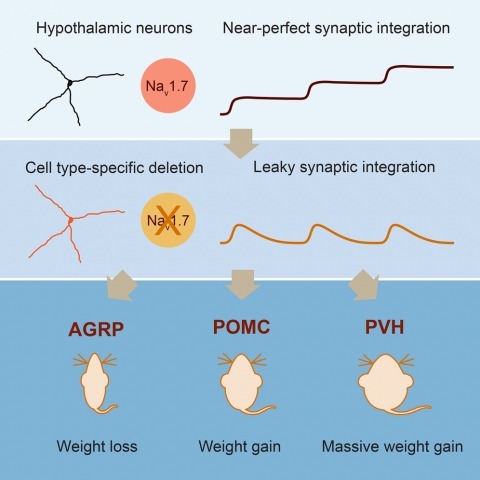
Neurons are well suited for computations on millisecond timescales, but some neuronal circuits set behavioral states over long time periods, such as those involved in energy homeostasis. We found that multiple types of hypothalamic neurons, including those that oppositely regulate body weight, are specialized as near-perfect synaptic integrators that summate inputs over extended timescales. Excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) are greatly prolonged, outlasting the neuronal membrane time-constant up to 10-fold. This is due to the voltage-gated sodium channel Nav1.7 (Scn9a), previously associated with pain-sensation but not synaptic integration. Scn9a deletion in AGRP, POMC, or paraventricular hypothalamic neurons reduced EPSP duration, synaptic integration, and altered body weight in mice. In vivo whole-cell recordings in the hypothalamus confirmed near-perfect synaptic integration. These experiments show that integration of synaptic inputs over time by Nav1.7 is critical for body weight regulation and reveal a mechanism for synaptic control of circuits regulating long term homeostatic functions.
Presynaptic, electron-dense, cytoplasmic protrusions such as the T-bar (Drosophila) or ribbon (vertebrates) are believed to facilitate vesicle movement to the active zone (AZ) of synapses throughout the nervous system. The molecular composition of these structures including the T-bar and ribbon are largely unknown, as are the mechanisms that specify their synapse-specific assembly and distribution. In a large-scale, forward genetic screen, we have identified a mutation termed air traffic controller (atc) that causes T-bar-like protein aggregates to form abnormally in motoneuron axons. This mutation disrupts a gene that encodes for a serine-arginine protein kinase (SRPK79D). This mutant phenotype is specific to SRPK79D and is not secondary to impaired kinesin-dependent axonal transport. The srpk79D gene is neuronally expressed, and transgenic rescue experiments are consistent with SRPK79D kinase activity being necessary in neurons. The SRPK79D protein colocalizes with the T-bar-associated protein Bruchpilot (Brp) in both the axon and synapse. We propose that SRPK79D is a novel T-bar-associated protein kinase that represses T-bar assembly in peripheral axons, and that SRPK79D-dependent repression must be relieved to facilitate site-specific AZ assembly. Consistent with this model, overexpression of SRPK79D disrupts AZ-specific Brp organization and significantly impairs presynaptic neurotransmitter release. These data identify a novel AZ-associated protein kinase and reveal a new mechanism of negative regulation involved in AZ assembly. This mechanism could contribute to the speed and specificity with which AZs are assembled throughout the nervous system.
Perceptual success depends on fast-spiking, parvalbumin-positive interneurons (FS/PVs). However, competing theories of optimal rate and correlation in pyramidal (PYR) firing make opposing predictions regarding the underlying FS/PV dynamics. We addressed this with population calcium imaging of FS/PVs and putative PYR neurons during threshold detection. In primary somatosensory and visual neocortex, a distinct PYR subset shows increased rate and spike-count correlations on detected trials ("hits"), while most show no rate change and decreased correlations. A larger fraction of FS/PVs predicts hits with either rate increases or decreases. Using computational modeling, we found that inhibitory imbalance, created by excitatory "feedback" and interactions between FS/PV pools, can account for the data. Rate-decreasing FS/PVs increase rate and correlation in a PYR subset, while rate-increasing FS/PVs reduce correlations and offset enhanced excitation in PYR neurons. These findings indicate that selection of informative PYR ensembles, through transient inhibitory imbalance, is a common motif of optimal neocortical processing.
Many motor control systems generate multiple movements using a common set of muscles. How are premotor circuits able to flexibly generate diverse movement patterns? Here, we characterize the neuronal circuits that drive the distinct courtship songs of Drosophila melanogaster. Male flies vibrate their wings towards females to produce two different song modes – pulse and sine song – which signal species identity and male quality. Using cell-type specific genetic reagents and the connectome, we provide a cellular and synaptic map of the circuits in the male ventral nerve cord that generate these songs and examine how activating or inhibiting each cell type within these circuits affects the song. Our data reveal that the song circuit is organized into two nested feed-forward pathways, with extensive reciprocal and feed-back connections. The larger network produces pulse song, the more complex and ancestral song form. A subset of this network produces sine song, the simpler and more recent form. Such nested organization may be a common feature of motor control circuits in which evolution has layered increasing flexibility on to a basic movement pattern.
In the cerebral cortex, local circuits consist of tens of thousands of neurons, each of which makes thousands of synaptic connections. Perhaps the biggest impediment to understanding these networks is that we have no wiring diagrams of their interconnections. Even if we had a partial or complete wiring diagram, however, understanding the network would also require information about each neuron’s function. Here we show that the relationship between structure and function can be studied in the cortex with a combination of in vivo physiology and network anatomy. We used two-photon calcium imaging to characterize a functional property–the preferred stimulus orientation–of a group of neurons in the mouse primary visual cortex. Large-scale electron microscopy of serial thin sections was then used to trace a portion of these neurons’ local network. Consistent with a prediction from recent physiological experiments, inhibitory interneurons received convergent anatomical input from nearby excitatory neurons with a broad range of preferred orientations, although weak biases could not be rejected.
Although hippocampal theta oscillations represent a prime example of temporal coding in the mammalian brain, little is known about the specific biophysical mechanisms. Intracellular recordings support a particular abstract oscillatory interference model of hippocampal theta activity, the soma-dendrite interference model. To gain insight into the cellular and circuit level mechanisms of theta activity, we implemented a similar form of interference using the actual hippocampal network in mice in vitro. We found that pairing increasing levels of phasic dendritic excitation with phasic stimulation of perisomatic projecting inhibitory interneurons induced a somatic polarization and action potential timing profile that reproduced most common features. Alterations in the temporal profile of inhibition were required to fully capture all features. These data suggest that theta-related place cell activity is generated through an interaction between a phasic dendritic excitation and a phasic perisomatic shunting inhibition delivered by interneurons, a subset of which undergo activity-dependent presynaptic modulation.
Complex networks are studied across many fields of science. To uncover their structural design principles, we defined “network motifs,” patterns of interconnections occurring in complex networks at numbers that are significantly higher than those in randomized networks. We found such motifs in networks from biochemistry, neurobiology, ecology, and engineering. The motifs shared by ecological food webs were distinct from the motifs shared by the genetic networks of Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae or from those found in the World Wide Web. Similar motifs were found in networks that perform information processing, even though they describe elements as different as biomolecules within a cell and synaptic connections between neurons in Caenorhabditis elegans. Motifs may thus define universal classes of networks. This approach may uncover the basic building blocks of most networks.
Regions within the prefrontal cortex are thought to process beliefs about the world, but little is known about the circuit dynamics underlying the formation and modification of these beliefs. Using a task that permits dissociation between the activity encoding an animal’s internal state and that encoding aspects of behavior, we found that transient increases in the volatility of activity in the rat medial prefrontal cortex accompany periods when an animal’s belief is modified after an environmental change. Activity across the majority of sampled neurons underwent marked, abrupt, and coordinated changes when prior belief was abandoned in favor of exploration of alternative strategies. These dynamics reflect network switches to a state of instability, which diminishes over the period of exploration as new stable representations are formed.