Filter
Associated Lab
- Aguilera Castrejon Lab (15) Apply Aguilera Castrejon Lab filter
- Ahrens Lab (56) Apply Ahrens Lab filter
- Aso Lab (39) Apply Aso Lab filter
- Baker Lab (38) Apply Baker Lab filter
- Betzig Lab (110) Apply Betzig Lab filter
- Beyene Lab (10) Apply Beyene Lab filter
- Bock Lab (17) Apply Bock Lab filter
- Branson Lab (48) Apply Branson Lab filter
- Card Lab (40) Apply Card Lab filter
- Cardona Lab (63) Apply Cardona Lab filter
- Chklovskii Lab (13) Apply Chklovskii Lab filter
- Clapham Lab (12) Apply Clapham Lab filter
- Cui Lab (19) Apply Cui Lab filter
- Darshan Lab (12) Apply Darshan Lab filter
- Dennis Lab (1) Apply Dennis Lab filter
- Dickson Lab (46) Apply Dickson Lab filter
- Druckmann Lab (25) Apply Druckmann Lab filter
- Dudman Lab (46) Apply Dudman Lab filter
- Eddy/Rivas Lab (30) Apply Eddy/Rivas Lab filter
- Egnor Lab (11) Apply Egnor Lab filter
- Espinosa Medina Lab (16) Apply Espinosa Medina Lab filter
- Feliciano Lab (6) Apply Feliciano Lab filter
- Fetter Lab (41) Apply Fetter Lab filter
- Fitzgerald Lab (28) Apply Fitzgerald Lab filter
- Freeman Lab (15) Apply Freeman Lab filter
- Funke Lab (34) Apply Funke Lab filter
- Gonen Lab (91) Apply Gonen Lab filter
- Grigorieff Lab (62) Apply Grigorieff Lab filter
- Harris Lab (58) Apply Harris Lab filter
- Heberlein Lab (94) Apply Heberlein Lab filter
- Hermundstad Lab (22) Apply Hermundstad Lab filter
- Hess Lab (71) Apply Hess Lab filter
- Ilanges Lab (1) Apply Ilanges Lab filter
- Jayaraman Lab (44) Apply Jayaraman Lab filter
- Ji Lab (33) Apply Ji Lab filter
- Johnson Lab (6) Apply Johnson Lab filter
- Kainmueller Lab (19) Apply Kainmueller Lab filter
- Karpova Lab (14) Apply Karpova Lab filter
- Keleman Lab (13) Apply Keleman Lab filter
- Keller Lab (75) Apply Keller Lab filter
- Koay Lab (16) Apply Koay Lab filter
- Lavis Lab (136) Apply Lavis Lab filter
- Lee (Albert) Lab (34) Apply Lee (Albert) Lab filter
- Leonardo Lab (23) Apply Leonardo Lab filter
- Li Lab (25) Apply Li Lab filter
- Lippincott-Schwartz Lab (161) Apply Lippincott-Schwartz Lab filter
- Liu (Yin) Lab (5) Apply Liu (Yin) Lab filter
- Liu (Zhe) Lab (58) Apply Liu (Zhe) Lab filter
- Looger Lab (137) Apply Looger Lab filter
- Magee Lab (49) Apply Magee Lab filter
- Menon Lab (18) Apply Menon Lab filter
- Murphy Lab (13) Apply Murphy Lab filter
- O'Shea Lab (4) Apply O'Shea Lab filter
- Otopalik Lab (13) Apply Otopalik Lab filter
- Pachitariu Lab (41) Apply Pachitariu Lab filter
- Pastalkova Lab (18) Apply Pastalkova Lab filter
- Pavlopoulos Lab (19) Apply Pavlopoulos Lab filter
- Pedram Lab (14) Apply Pedram Lab filter
- Podgorski Lab (16) Apply Podgorski Lab filter
- Reiser Lab (49) Apply Reiser Lab filter
- Riddiford Lab (44) Apply Riddiford Lab filter
- Romani Lab (40) Apply Romani Lab filter
- Rubin Lab (139) Apply Rubin Lab filter
- Saalfeld Lab (60) Apply Saalfeld Lab filter
- Satou Lab (16) Apply Satou Lab filter
- Scheffer Lab (36) Apply Scheffer Lab filter
- Schreiter Lab (62) Apply Schreiter Lab filter
- Sgro Lab (20) Apply Sgro Lab filter
- Shroff Lab (23) Apply Shroff Lab filter
- Simpson Lab (23) Apply Simpson Lab filter
- Singer Lab (80) Apply Singer Lab filter
- Spruston Lab (91) Apply Spruston Lab filter
- Stern Lab (152) Apply Stern Lab filter
- Sternson Lab (54) Apply Sternson Lab filter
- Stringer Lab (29) Apply Stringer Lab filter
- Svoboda Lab (135) Apply Svoboda Lab filter
- Tebo Lab (31) Apply Tebo Lab filter
- Tervo Lab (9) Apply Tervo Lab filter
- Tillberg Lab (17) Apply Tillberg Lab filter
- Tjian Lab (64) Apply Tjian Lab filter
- Truman Lab (88) Apply Truman Lab filter
- Turaga Lab (46) Apply Turaga Lab filter
- Turner Lab (35) Apply Turner Lab filter
- Vale Lab (6) Apply Vale Lab filter
- Voigts Lab (2) Apply Voigts Lab filter
- Wang (Meng) Lab (9) Apply Wang (Meng) Lab filter
- Wang (Shaohe) Lab (24) Apply Wang (Shaohe) Lab filter
- Wu Lab (9) Apply Wu Lab filter
- Zlatic Lab (28) Apply Zlatic Lab filter
- Zuker Lab (25) Apply Zuker Lab filter
Associated Project Team
- CellMap (5) Apply CellMap filter
- COSEM (3) Apply COSEM filter
- Fly Descending Interneuron (10) Apply Fly Descending Interneuron filter
- Fly Functional Connectome (14) Apply Fly Functional Connectome filter
- Fly Olympiad (5) Apply Fly Olympiad filter
- FlyEM (51) Apply FlyEM filter
- FlyLight (46) Apply FlyLight filter
- GENIE (40) Apply GENIE filter
- Integrative Imaging (1) Apply Integrative Imaging filter
- Larval Olympiad (2) Apply Larval Olympiad filter
- MouseLight (16) Apply MouseLight filter
- NeuroSeq (1) Apply NeuroSeq filter
- ThalamoSeq (1) Apply ThalamoSeq filter
- Tool Translation Team (T3) (24) Apply Tool Translation Team (T3) filter
- Transcription Imaging (49) Apply Transcription Imaging filter
Publication Date
- 2024 (141) Apply 2024 filter
- 2023 (175) Apply 2023 filter
- 2022 (192) Apply 2022 filter
- 2021 (193) Apply 2021 filter
- 2020 (196) Apply 2020 filter
- 2019 (202) Apply 2019 filter
- 2018 (232) Apply 2018 filter
- 2017 (217) Apply 2017 filter
- 2016 (209) Apply 2016 filter
- 2015 (252) Apply 2015 filter
- 2014 (236) Apply 2014 filter
- 2013 (194) Apply 2013 filter
- 2012 (190) Apply 2012 filter
- 2011 (190) Apply 2011 filter
- 2010 (161) Apply 2010 filter
- 2009 (158) Apply 2009 filter
- 2008 (140) Apply 2008 filter
- 2007 (106) Apply 2007 filter
- 2006 (92) Apply 2006 filter
- 2005 (67) Apply 2005 filter
- 2004 (57) Apply 2004 filter
- 2003 (58) Apply 2003 filter
- 2002 (39) Apply 2002 filter
- 2001 (28) Apply 2001 filter
- 2000 (29) Apply 2000 filter
- 1999 (14) Apply 1999 filter
- 1998 (18) Apply 1998 filter
- 1997 (16) Apply 1997 filter
- 1996 (10) Apply 1996 filter
- 1995 (18) Apply 1995 filter
- 1994 (12) Apply 1994 filter
- 1993 (10) Apply 1993 filter
- 1992 (6) Apply 1992 filter
- 1991 (11) Apply 1991 filter
- 1990 (11) Apply 1990 filter
- 1989 (6) Apply 1989 filter
- 1988 (1) Apply 1988 filter
- 1987 (7) Apply 1987 filter
- 1986 (4) Apply 1986 filter
- 1985 (5) Apply 1985 filter
- 1984 (2) Apply 1984 filter
- 1983 (2) Apply 1983 filter
- 1982 (3) Apply 1982 filter
- 1981 (3) Apply 1981 filter
- 1980 (1) Apply 1980 filter
- 1979 (1) Apply 1979 filter
- 1976 (2) Apply 1976 filter
- 1973 (1) Apply 1973 filter
- 1970 (1) Apply 1970 filter
- 1967 (1) Apply 1967 filter
Type of Publication
3920 Publications
Showing 2901-2910 of 3920 resultsPopulation neural recordings with long-range temporal structure are often best understood in terms of a shared underlying low-dimensional dynamical process. Advances in recording technology provide access to an ever larger fraction of the population, but the standard computational approaches available to identify the collective dynamics scale poorly with the size of the dataset. Here we describe a new, scalable approach to discovering the low-dimensional dynamics that underlie simultaneously recorded spike trains from a neural population. Our method is based on recurrent linear models (RLMs), and relates closely to timeseries models based on recurrent neural networks. We formulate RLMs for neural data by generalising the Kalman-filter-based likelihood calculation for latent linear dynamical systems (LDS) models to incorporate a generalised-linear observation process. We show that RLMs describe motor-cortical population data better than either directly-coupled generalised-linear models or latent linear dynamical system models with generalised-linear observations. We also introduce the cascaded linear model (CLM) to capture low-dimensional instantaneous correlations in neural populations. The CLM describes the cortical recordings better than either Ising or Gaussian models and, like the RLM, can be fit exactly and quickly. The CLM can also be seen as a generalization of a low-rank Gaussian model, in this case factor analysis. The computational tractability of the RLM and CLM allow both to scale to very high-dimensional neural data.
Traditional approaches for increasing the affinity of protein-protein complexes focus on constructing highly complementary binding surfaces. Recent theoretical simulations and experimental results suggest that electrostatic steering forces can also be manipulated to increase association rates while leaving dissociation rates unchanged, thus increasing affinity. Here we demonstrate that electrostatic attraction can be enhanced between an antibody fragment and its cognate antigen through application of a few simple rules to identify potential on-rate amplification sites that lie at the periphery of the antigen-antibody interface.
We developed a series of statistical potentials to recognize the native protein from decoys, particularly when using only a reduced representation in which each side chain is treated as a single C(beta) atom. Beginning with a highly successful all-atom statistical potential, the Discrete Optimized Protein Energy function (DOPE), we considered the implications of including additional information in the all-atom statistical potential and subsequently reducing to the C(beta) representation. One of the potentials includes interaction energies conditional on backbone geometries. A second potential separates sequence local from sequence nonlocal interactions and introduces a novel reference state for the sequence local interactions. The resultant potentials perform better than the original DOPE statistical potential in decoy identification. Moreover, even upon passing to a reduced C(beta) representation, these statistical potentials outscore the original (all-atom) DOPE potential in identifying native states for sets of decoys. Interestingly, the backbone-dependent statistical potential is shown to retain nearly all of the information content of the all-atom representation in the C(beta) representation. In addition, these new statistical potentials are combined with existing potentials to model hydrogen bonding, torsion energies, and solvation energies to produce even better performing potentials. The ability of the C(beta) statistical potentials to accurately represent protein interactions bodes well for computational efficiency in protein folding calculations using reduced backbone representations, while the extensions to DOPE illustrate general principles for improving knowledge-based potentials.
Endocytic recycling of synaptic vesicles after exocytosis is critical for nervous system function. At synapses of cultured neurons that lack the two "neuronal" dynamins, dynamin 1 and 3, smaller excitatory postsynaptic currents are observed due to an impairment of the fission reaction of endocytosis that results in an accumulation of arrested clathrin-coated pits and a greatly reduced synaptic vesicle number. Surprisingly, despite a smaller readily releasable vesicle pool and fewer docked vesicles, a strong facilitation, which correlated with lower vesicle release probability, was observed upon action potential stimulation at such synapses. Furthermore, although network activity in mutant cultures was lower, Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) activity was unexpectedly increased, consistent with the previous report of an enhanced state of synapsin 1 phosphorylation at CaMKII-dependent sites in such neurons. These changes were partially reversed by overnight silencing of synaptic activity with tetrodotoxin, a treatment that allows progression of arrested endocytic pits to synaptic vesicles. Facilitation was also counteracted by CaMKII inhibition. These findings reveal a mechanism aimed at preventing synaptic transmission failure due to vesicle depletion when recycling vesicle traffic is backed up by a defect in dynamin-dependent endocytosis and provide new insight into the coupling between endocytosis and exocytosis.
The Ssn6-Tup1 corepressor complex regulates many genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Three mechanisms have been proposed to explain its repression functions: 1) nucleosome positioning by binding histone tails; 2) recruitment of histone deacetylases; and 3) direct interference with the general transcription machinery or activators. It is unclear if Ssn6-Tup1 utilizes each of these mechanisms at a single gene in a redundant manner or each individually at different loci. A systematic analysis of the contribution of each mechanism at a native promoter has not been reported. Here we employed a genetic strategy to analyze the contributions of nucleosome positioning, histone deacetylation, and Mediator interference in the repression of chromosomal Tup1 target genes in vivo. We exploited the fact that Ssn6-Tup1 requires the ISW2 chromatin remodeling complex to establish nucleosome positioning in vivo to disrupt chromatin structure without affecting other Tup1 repression functions. Deleting ISW2, the histone deacetylase gene HDA1, or genes encoding Mediator subunits individually caused slight or no derepression of RNR3 and HUG1. However, when Mediator mutations were combined with Deltaisw2 or Deltahda1 mutations, enhanced transcription was observed, and the strongest level of derepression was observed in triple Deltaisw2/Deltahda1/Mediator mutants. The increased transcription in the mutants was not due to the loss of Tup1 at the promoter and correlated with increased TBP cross-linking to promoters. Thus, Tup1 utilizes multiple redundant mechanisms to repress transcription of native genes, which may be important for it to act as a global corepressor at a wide variety of promoters.
Regulated gene expression is a complex process achieved through the function of multiple protein factors acting in concert at a given promoter. The transcription factor TFIID is a central component of the machinery regulating mRNA synthesis by RNA polymerase II. This large multiprotein complex is composed of the TATA box binding protein (TBP) and several TBP-associated factors (TAF(II)s). The recent discovery of multiple TBP-related factors and tissue-specific TAF(II)s suggests the existence of specialized TFIID complexes that likely play a critical role in regulating transcription in a gene- and tissue-specific manner. The tissue-selective factor TAF(II)105 was originally identified as a component of TFIID derived from a human B-cell line. In this report we demonstrate the specific induction of TAF(II)105 in cultured B cells in response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS). To examine the in vivo role of TAF(II)105, we have generated TAF(II)105-null mice by homologous recombination. Here we show that B-lymphocyte development is largely unaffected by the absence of TAF(II)105. TAF(II)105-null B cells can proliferate in response to LPS, produce relatively normal levels of resting antibodies, and can mount an immune response by producing antigen-specific antibodies in response to immunization. Taken together, we conclude that the function of TAF(II)105 in B cells is likely redundant with the function of other TAF(II)105-related cellular proteins.
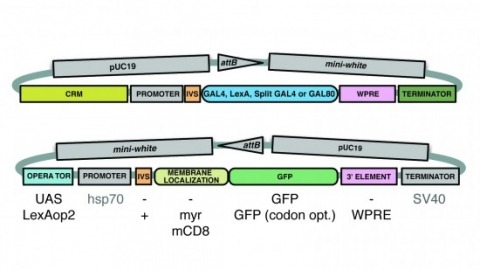
A wide variety of biological experiments rely on the ability to express an exogenous gene in a transgenic animal at a defined level and in a spatially and temporally controlled pattern. We describe major improvements of the methods available for achieving this objective in Drosophila melanogaster. We have systematically varied core promoters, UTRs, operator sequences, and transcriptional activating domains used to direct gene expression with the GAL4, LexA, and Split GAL4 transcription factors and the GAL80 transcriptional repressor. The use of site-specific integration allowed us to make quantitative comparisons between different constructs inserted at the same genomic location. We also characterized a set of PhiC31 integration sites for their ability to support transgene expression of both drivers and responders in the nervous system. The increased strength and reliability of these optimized reagents overcome many of the previous limitations of these methods and will facilitate genetic manipulations of greater complexity and sophistication.
Many animal embryos face early on in development the problem of having to pull and close an epithelial sheet around the spherical yolk-sac. During this gastrulation process, known as epiboly, the spherical geometry of the egg dictates that the epithelial sheet first expands and subsequently compacts to close around the sphere. While it is well recognized that contractile actomyosin cables can drive epiboly movements, it is unclear how pulling on the leading edge can lead to simultaneous tissue expansion and compaction. Moreover, the epithelial sheet spreading over the sphere is mechanically stressed and this stress needs to be dissipated for seamless closure. While oriented cell division is known to dissipate tissue stresses during epiboly, it is unclear how this can be achieved without cell division. Here we show that during extraembryonic tissue (serosa) epiboly in the red flour beetle Tribolium castaneum, the non-proliferative serosa becomes regionalized into two distinct territories: a dorsal region under higher tension away from the leading edge with larger, isodiametric and non-rearranging cells, and a more fluid ventral region under lower tension surrounding the leading edge with smaller, anisotropic cells undergoing cell intercalation. Our results suggest that fluidization of the leading edge is effected by a heterogeneous actomyosin cable that drives sequential eviction and intercalation of individual cells away from the serosa margin. Since this developmental solution utilized during epiboly resembles the mechanism of wound healing in other systems, we propose actomyosin cable-driven local tissue fluidization as a conserved morphogenetic module for closure of epithelial gaps.
Most functional plasticity studies in the cortex have focused on layers (L) II/III and IV, whereas relatively little is known of LV. Structural measurements of dendritic spines in vivo suggest some specialization among LV cell subtypes. We therefore studied experience-dependent plasticity in the barrel cortex using intracellular recordings to distinguish regular spiking (RS) and intrinsic bursting (IB) subtypes. Postsynaptic potentials and suprathreshold responses in vivo revealed a remarkable dichotomy in RS and IB cell plasticity; spared whisker potentiation occurred in IB but not RS cells while deprived whisker depression occurred in RS but not IB cells. Similar RS/IB differences were found in the LII/III to V connections in brain slices. Modeling studies showed that subthreshold changes predicted the suprathreshold changes. These studies demonstrate the major functional partition of plasticity within a single cortical layer and reveal the LII/III to LV connection as a major excitatory locus of cortical plasticity.
Neural language models (LMs) based on recurrent neural networks (RNN) are some of the most successful word and character-level LMs. Why do they work so well, in particular better than linear neural LMs? Possible explanations are that RNNs have an implicitly better regularization or that RNNs have a higher capacity for storing patterns due to their nonlinearities or both. Here we argue for the first explanation in the limit of little training data and the second explanation for large amounts of text data. We show state-of-the-art performance on the popular and small Penn dataset when RNN LMs are regularized with random dropout. Nonetheless, we show even better performance from a simplified, much less expressive linear RNN model without off-diagonal entries in the recurrent matrix. We call this model an impulse-response LM (IRLM). Using random dropout, column normalization and annealed learning rates, IRLMs develop neurons that keep a memory of up to 50 words in the past and achieve a perplexity of 102.5 on the Penn dataset. On two large datasets however, the same regularization methods are unsuccessful for both models and the RNN's expressivity allows it to overtake the IRLM by 10 and 20 percent perplexity, respectively. Despite the perplexity gap, IRLMs still outperform RNNs on the Microsoft Research Sentence Completion (MRSC) task. We develop a slightly modified IRLM that separates long-context units (LCUs) from short-context units and show that the LCUs alone achieve a state-of-the-art performance on the MRSC task of 60.8%. Our analysis indicates that a fruitful direction of research for neural LMs lies in developing more accessible internal representations, and suggests an optimization regime of very high momentum terms for effectively training such models.