Filter
Associated Lab
- Aguilera Castrejon Lab (15) Apply Aguilera Castrejon Lab filter
- Ahrens Lab (57) Apply Ahrens Lab filter
- Aso Lab (39) Apply Aso Lab filter
- Baker Lab (38) Apply Baker Lab filter
- Betzig Lab (111) Apply Betzig Lab filter
- Beyene Lab (10) Apply Beyene Lab filter
- Bock Lab (17) Apply Bock Lab filter
- Branson Lab (48) Apply Branson Lab filter
- Card Lab (40) Apply Card Lab filter
- Cardona Lab (63) Apply Cardona Lab filter
- Chklovskii Lab (13) Apply Chklovskii Lab filter
- Clapham Lab (13) Apply Clapham Lab filter
- Cui Lab (19) Apply Cui Lab filter
- Darshan Lab (12) Apply Darshan Lab filter
- Dennis Lab (1) Apply Dennis Lab filter
- Dickson Lab (46) Apply Dickson Lab filter
- Druckmann Lab (25) Apply Druckmann Lab filter
- Dudman Lab (46) Apply Dudman Lab filter
- Eddy/Rivas Lab (30) Apply Eddy/Rivas Lab filter
- Egnor Lab (11) Apply Egnor Lab filter
- Espinosa Medina Lab (16) Apply Espinosa Medina Lab filter
- Feliciano Lab (6) Apply Feliciano Lab filter
- Fetter Lab (41) Apply Fetter Lab filter
- Fitzgerald Lab (28) Apply Fitzgerald Lab filter
- Freeman Lab (15) Apply Freeman Lab filter
- Funke Lab (35) Apply Funke Lab filter
- Gonen Lab (91) Apply Gonen Lab filter
- Grigorieff Lab (62) Apply Grigorieff Lab filter
- Harris Lab (58) Apply Harris Lab filter
- Heberlein Lab (94) Apply Heberlein Lab filter
- Hermundstad Lab (22) Apply Hermundstad Lab filter
- Hess Lab (72) Apply Hess Lab filter
- Ilanges Lab (1) Apply Ilanges Lab filter
- Jayaraman Lab (44) Apply Jayaraman Lab filter
- Ji Lab (33) Apply Ji Lab filter
- Johnson Lab (6) Apply Johnson Lab filter
- Kainmueller Lab (19) Apply Kainmueller Lab filter
- Karpova Lab (14) Apply Karpova Lab filter
- Keleman Lab (13) Apply Keleman Lab filter
- Keller Lab (75) Apply Keller Lab filter
- Koay Lab (17) Apply Koay Lab filter
- Lavis Lab (138) Apply Lavis Lab filter
- Lee (Albert) Lab (34) Apply Lee (Albert) Lab filter
- Leonardo Lab (23) Apply Leonardo Lab filter
- Li Lab (27) Apply Li Lab filter
- Lippincott-Schwartz Lab (161) Apply Lippincott-Schwartz Lab filter
- Liu (Yin) Lab (5) Apply Liu (Yin) Lab filter
- Liu (Zhe) Lab (61) Apply Liu (Zhe) Lab filter
- Looger Lab (137) Apply Looger Lab filter
- Magee Lab (49) Apply Magee Lab filter
- Menon Lab (18) Apply Menon Lab filter
- Murphy Lab (13) Apply Murphy Lab filter
- O'Shea Lab (6) Apply O'Shea Lab filter
- Otopalik Lab (13) Apply Otopalik Lab filter
- Pachitariu Lab (42) Apply Pachitariu Lab filter
- Pastalkova Lab (18) Apply Pastalkova Lab filter
- Pavlopoulos Lab (19) Apply Pavlopoulos Lab filter
- Pedram Lab (14) Apply Pedram Lab filter
- Podgorski Lab (16) Apply Podgorski Lab filter
- Reiser Lab (49) Apply Reiser Lab filter
- Riddiford Lab (44) Apply Riddiford Lab filter
- Romani Lab (41) Apply Romani Lab filter
- Rubin Lab (139) Apply Rubin Lab filter
- Saalfeld Lab (61) Apply Saalfeld Lab filter
- Satou Lab (16) Apply Satou Lab filter
- Scheffer Lab (36) Apply Scheffer Lab filter
- Schreiter Lab (62) Apply Schreiter Lab filter
- Sgro Lab (20) Apply Sgro Lab filter
- Shroff Lab (24) Apply Shroff Lab filter
- Simpson Lab (23) Apply Simpson Lab filter
- Singer Lab (80) Apply Singer Lab filter
- Spruston Lab (91) Apply Spruston Lab filter
- Stern Lab (152) Apply Stern Lab filter
- Sternson Lab (54) Apply Sternson Lab filter
- Stringer Lab (29) Apply Stringer Lab filter
- Svoboda Lab (135) Apply Svoboda Lab filter
- Tebo Lab (31) Apply Tebo Lab filter
- Tervo Lab (9) Apply Tervo Lab filter
- Tillberg Lab (17) Apply Tillberg Lab filter
- Tjian Lab (64) Apply Tjian Lab filter
- Truman Lab (88) Apply Truman Lab filter
- Turaga Lab (46) Apply Turaga Lab filter
- Turner Lab (35) Apply Turner Lab filter
- Vale Lab (6) Apply Vale Lab filter
- Voigts Lab (2) Apply Voigts Lab filter
- Wang (Meng) Lab (10) Apply Wang (Meng) Lab filter
- Wang (Shaohe) Lab (24) Apply Wang (Shaohe) Lab filter
- Wu Lab (9) Apply Wu Lab filter
- Zlatic Lab (28) Apply Zlatic Lab filter
- Zuker Lab (25) Apply Zuker Lab filter
Associated Project Team
- CellMap (6) Apply CellMap filter
- COSEM (3) Apply COSEM filter
- Fly Descending Interneuron (10) Apply Fly Descending Interneuron filter
- Fly Functional Connectome (14) Apply Fly Functional Connectome filter
- Fly Olympiad (5) Apply Fly Olympiad filter
- FlyEM (51) Apply FlyEM filter
- FlyLight (46) Apply FlyLight filter
- GENIE (40) Apply GENIE filter
- Integrative Imaging (1) Apply Integrative Imaging filter
- Larval Olympiad (2) Apply Larval Olympiad filter
- MouseLight (16) Apply MouseLight filter
- NeuroSeq (1) Apply NeuroSeq filter
- ThalamoSeq (1) Apply ThalamoSeq filter
- Tool Translation Team (T3) (24) Apply Tool Translation Team (T3) filter
- Transcription Imaging (49) Apply Transcription Imaging filter
Publication Date
- 2024 (170) Apply 2024 filter
- 2023 (171) Apply 2023 filter
- 2022 (192) Apply 2022 filter
- 2021 (193) Apply 2021 filter
- 2020 (196) Apply 2020 filter
- 2019 (202) Apply 2019 filter
- 2018 (232) Apply 2018 filter
- 2017 (217) Apply 2017 filter
- 2016 (209) Apply 2016 filter
- 2015 (252) Apply 2015 filter
- 2014 (236) Apply 2014 filter
- 2013 (194) Apply 2013 filter
- 2012 (190) Apply 2012 filter
- 2011 (190) Apply 2011 filter
- 2010 (161) Apply 2010 filter
- 2009 (158) Apply 2009 filter
- 2008 (140) Apply 2008 filter
- 2007 (106) Apply 2007 filter
- 2006 (92) Apply 2006 filter
- 2005 (67) Apply 2005 filter
- 2004 (57) Apply 2004 filter
- 2003 (58) Apply 2003 filter
- 2002 (39) Apply 2002 filter
- 2001 (28) Apply 2001 filter
- 2000 (29) Apply 2000 filter
- 1999 (14) Apply 1999 filter
- 1998 (18) Apply 1998 filter
- 1997 (16) Apply 1997 filter
- 1996 (10) Apply 1996 filter
- 1995 (18) Apply 1995 filter
- 1994 (12) Apply 1994 filter
- 1993 (10) Apply 1993 filter
- 1992 (6) Apply 1992 filter
- 1991 (11) Apply 1991 filter
- 1990 (11) Apply 1990 filter
- 1989 (6) Apply 1989 filter
- 1988 (1) Apply 1988 filter
- 1987 (7) Apply 1987 filter
- 1986 (4) Apply 1986 filter
- 1985 (5) Apply 1985 filter
- 1984 (2) Apply 1984 filter
- 1983 (2) Apply 1983 filter
- 1982 (3) Apply 1982 filter
- 1981 (3) Apply 1981 filter
- 1980 (1) Apply 1980 filter
- 1979 (1) Apply 1979 filter
- 1976 (2) Apply 1976 filter
- 1973 (1) Apply 1973 filter
- 1970 (1) Apply 1970 filter
- 1967 (1) Apply 1967 filter
Type of Publication
3945 Publications
Showing 1711-1720 of 3945 resultsThe recent derivation of human trophoblast stem cells (TSCs) from placental cytotrophoblasts and blastocysts opened opportunities for studying the development and function of the human placenta. Recent reports have suggested that human naïve, but not primed, pluripotent stem cells (PSCs) retain an exclusive potential to generate TSCs. Here we report that, in the absence of WNT stimulation, transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) pathway inhibition leads to direct and robust conversion of primed human PSCs into TSCs. The resulting primed PSC-derived TSC lines exhibit self-renewal, can differentiate into the main trophoblast lineages, and present RNA and epigenetic profiles that are indistinguishable from recently established TSC lines derived from human placenta, blastocysts, or isogenic human naïve PSCs expanded under human enhanced naïve stem cell medium (HENSM) conditions. Activation of nuclear Yes-associated protein (YAP) signaling is sufficient for this conversion and necessary for human TSC maintenance. Our findings underscore a residual plasticity in primed human PSCs that allows their in vitro conversion into extra-embryonic trophoblast lineages.
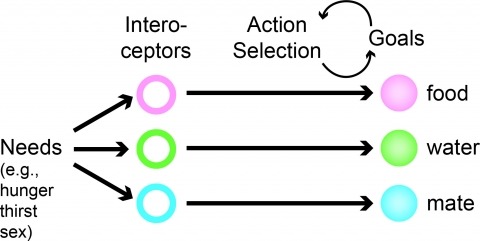
Physiological need states direct decision-making toward re-establishing homeostasis. Using a two-alternative forced choice task for mice that models elements of human decisions, we found that varying hunger and thirst states caused need-inappropriate choices, such as food seeking when thirsty. These results show limits on interoceptive knowledge of hunger and thirst states to guide decision-making. Instead, need states were identified after food and water consumption by outcome evaluation, which depended on the medial prefrontal cortex.
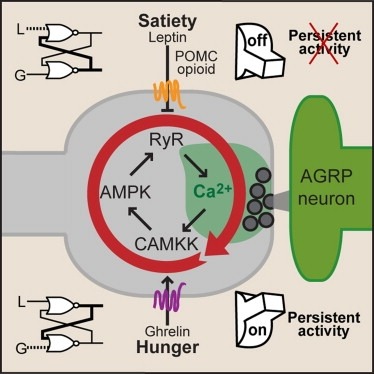
Synaptic plasticity in response to changes in physiologic state is coordinated by hormonal signals across multiple neuronal cell types. Here, we combine cell-type-specific electrophysiological, pharmacological, and optogenetic techniques to dissect neural circuits and molecular pathways controlling synaptic plasticity onto AGRP neurons, a population that regulates feeding. We find that food deprivation elevates excitatory synaptic input, which is mediated by a presynaptic positive feedback loop involving AMP-activated protein kinase. Potentiation of glutamate release was triggered by the orexigenic hormone ghrelin and exhibited hysteresis, persisting for hours after ghrelin removal. Persistent activity was reversed by the anorexigenic hormone leptin, and optogenetic photostimulation demonstrated involvement of opioid release from POMC neurons. Based on these experiments, we propose a memory storage device for physiological state constructed from bistable synapses that are flipped between two sustained activity states by transient exposure to hormones signaling energy levels.
Posttranslational modification through palmitoylation regulates protein localization and function. In this study, we identify a role for the Drosophila melanogaster palmitoyl transferase Huntingtin-interacting protein 14 (HIP14) in neurotransmitter release. hip14 mutants show exocytic defects at low frequency stimulation and a nearly complete loss of synaptic transmission at higher temperature. Interestingly, two exocytic components known to be palmitoylated, cysteine string protein (CSP) and SNAP25, are severely mislocalized at hip14 mutant synapses. Complementary DNA rescue and localization experiments indicate that HIP14 is required solely in the nervous system and is essential for presynaptic function. Biochemical studies indicate that HIP14 palmitoylates CSP and that CSP is not palmitoylated in hip14 mutants. Furthermore, the hip14 exocytic defects can be suppressed by targeting CSP to synaptic vesicles using a chimeric protein approach. Our data indicate that HIP14 controls neurotransmitter release by regulating the trafficking of CSP to synapses.
Circadian rhythms in animals are regulated at the level of individual cells and by systemic signaling to coordinate the activities of multiple tissues. The circadian pacemakers have several physiological outputs, including daily locomotor rhythms. Several redox-active compounds have been found to function in regulation of circadian rhythms in cells, however, how particular compounds might be involved in regulating specific animal behaviors remains largely unknown. Here the effects of hydrogen peroxide on Drosophila movement were analyzed using a recently developed three-dimensional real-time multiple fly tracking assay. Both hydrogen peroxide feeding and direct injection of hydrogen peroxide caused increased adult fly locomotor activity. Continuous treatment with hydrogen peroxide also suppressed daily locomotor rhythms. Conditional over-expression of the hydrogen peroxide-producing enzyme superoxide dismutase (SOD) also increased fly activity and altered the patterns of locomotor activity across days and weeks. The real-time fly tracking system allowed for detailed analysis of the effects of these manipulations on behavior. For example, both hydrogen peroxide feeding and SOD over-expression increased all fly motion parameters, however, hydrogen peroxide feeding caused relatively more erratic movement, whereas SOD over-expression produced relatively faster-moving flies. Taken together, the data demonstrate that hydrogen peroxide has dramatic effects on fly movement and daily locomotor rhythms, and implicate hydrogen peroxide in the normal control of these processes.
Specificity remains a major challenge to current therapeutic strategies for cancer. Mutation associated neoantigens (MANAs) are products of genetic alterations, making them highly specific therapeutic targets. MANAs are HLA-presented (pHLA) peptides derived from intracellular mutant proteins that are otherwise inaccessible to antibody-based therapeutics. Here, we describe the cryo-EM structure of an antibody-MANA pHLA complex. Specifically, we determine a TCR mimic (TCRm) antibody bound to its MANA target, the KRAS peptide presented by HLA-A*03:01. Hydrophobic residues appear to account for the specificity of the mutant G12V residue. We also determine the structure of the wild-type G12 peptide bound to HLA-A*03:01, using X-ray crystallography. Based on these structures, we perform screens to validate the key residues required for peptide specificity. These experiments led us to a model for discrimination between the mutant and the wild-type peptides presented on HLA-A*03:01 based exclusively on hydrophobic interactions.
Ethanol stimulates the firing activity of midbrain dopamine (DA) neurons, leading to enhanced dopaminergic transmission in the mesolimbic system. This effect is thought to underlie the behavioral reinforcement of alcohol intake. Ethanol has been shown to directly enhance the intrinsic pacemaker activity of DA neurons, yet the cellular mechanism mediating this excitation remains poorly understood. The hyperpolarization-activated cation current, Ih, is known to contribute to the pacemaker firing of DA neurons. To determine the role of Ih in ethanol excitation of DA neurons, we performed patch-clamp recordings in acutely prepared mouse midbrain slices. Superfusion of ethanol increased the spontaneous firing frequency of DA neurons in a reversible fashion. Treatment with ZD7288, a blocker of Ih, irreversibly depressed basal firing frequency and significantly attenuated the stimulatory effect of ethanol on firing. Furthermore, ethanol reversibly augmented Ih amplitude and accelerated its activation kinetics. This effect of ethanol was accompanied by a shift in the voltage dependence of Ih activation to more depolarized potentials and an increase in the maximum Ih conductance. Cyclic AMP mediated the depolarizing shift in Ih activation but not the increase in the maximum conductance. Finally, repeated ethanol treatment in vivo induced downregulation of Ih density in DA neurons and an accompanying reduction in the magnitude of ethanol stimulation of firing. These results suggest an important role of Ih in the reinforcing actions of ethanol and in the neuroadaptations underlying escalation of alcohol consumption associated with alcoholism.
Neural processes that direct an animal’s actions toward environmental goals are critical elements for understanding behavior. The hypothalamus is closely associated with motivated behaviors required for survival and reproduction. Intense feeding, drinking, aggressive, and sexual behaviors can be produced by a simple neuronal stimulus applied to discrete hypothalamic regions. What can these "evoked behaviors" teach us about the neural processes that determine behavioral intent and intensity? Small populations of neurons sufficient to evoke a complex motivated behavior may be used as entry points to identify circuits that energize and direct behavior to specific goals. Here, I review recent applications of molecular genetic, optogenetic, and pharmacogenetic approaches that overcome previous limitations for analyzing anatomically complex hypothalamic circuits and their interactions with the rest of the brain. These new tools have the potential to bridge the gaps between neurobiological and psychological thinking about the mechanisms of complex motivated behavior.