Filter
Associated Lab
- Aguilera Castrejon Lab (17) Apply Aguilera Castrejon Lab filter
- Ahrens Lab (68) Apply Ahrens Lab filter
- Aso Lab (42) Apply Aso Lab filter
- Baker Lab (38) Apply Baker Lab filter
- Betzig Lab (115) Apply Betzig Lab filter
- Beyene Lab (14) Apply Beyene Lab filter
- Bock Lab (17) Apply Bock Lab filter
- Branson Lab (54) Apply Branson Lab filter
- Card Lab (43) Apply Card Lab filter
- Cardona Lab (64) Apply Cardona Lab filter
- Chklovskii Lab (13) Apply Chklovskii Lab filter
- Clapham Lab (15) Apply Clapham Lab filter
- Cui Lab (19) Apply Cui Lab filter
- Darshan Lab (12) Apply Darshan Lab filter
- Dennis Lab (1) Apply Dennis Lab filter
- Dickson Lab (46) Apply Dickson Lab filter
- Druckmann Lab (25) Apply Druckmann Lab filter
- Dudman Lab (52) Apply Dudman Lab filter
- Eddy/Rivas Lab (30) Apply Eddy/Rivas Lab filter
- Egnor Lab (11) Apply Egnor Lab filter
- Espinosa Medina Lab (20) Apply Espinosa Medina Lab filter
- Feliciano Lab (8) Apply Feliciano Lab filter
- Fetter Lab (41) Apply Fetter Lab filter
- FIB-SEM Technology (1) Apply FIB-SEM Technology filter
- Fitzgerald Lab (29) Apply Fitzgerald Lab filter
- Freeman Lab (15) Apply Freeman Lab filter
- Funke Lab (41) Apply Funke Lab filter
- Gonen Lab (91) Apply Gonen Lab filter
- Grigorieff Lab (62) Apply Grigorieff Lab filter
- Harris Lab (64) Apply Harris Lab filter
- Heberlein Lab (94) Apply Heberlein Lab filter
- Hermundstad Lab (29) Apply Hermundstad Lab filter
- Hess Lab (79) Apply Hess Lab filter
- Ilanges Lab (2) Apply Ilanges Lab filter
- Jayaraman Lab (47) Apply Jayaraman Lab filter
- Ji Lab (33) Apply Ji Lab filter
- Johnson Lab (6) Apply Johnson Lab filter
- Kainmueller Lab (19) Apply Kainmueller Lab filter
- Karpova Lab (14) Apply Karpova Lab filter
- Keleman Lab (13) Apply Keleman Lab filter
- Keller Lab (76) Apply Keller Lab filter
- Koay Lab (18) Apply Koay Lab filter
- Lavis Lab (152) Apply Lavis Lab filter
- Lee (Albert) Lab (34) Apply Lee (Albert) Lab filter
- Leonardo Lab (23) Apply Leonardo Lab filter
- Li Lab (29) Apply Li Lab filter
- Lippincott-Schwartz Lab (174) Apply Lippincott-Schwartz Lab filter
- Liu (Yin) Lab (7) Apply Liu (Yin) Lab filter
- Liu (Zhe) Lab (64) Apply Liu (Zhe) Lab filter
- Looger Lab (138) Apply Looger Lab filter
- Magee Lab (49) Apply Magee Lab filter
- Menon Lab (18) Apply Menon Lab filter
- Murphy Lab (13) Apply Murphy Lab filter
- O'Shea Lab (7) Apply O'Shea Lab filter
- Otopalik Lab (13) Apply Otopalik Lab filter
- Pachitariu Lab (49) Apply Pachitariu Lab filter
- Pastalkova Lab (18) Apply Pastalkova Lab filter
- Pavlopoulos Lab (19) Apply Pavlopoulos Lab filter
- Pedram Lab (15) Apply Pedram Lab filter
- Podgorski Lab (16) Apply Podgorski Lab filter
- Reiser Lab (52) Apply Reiser Lab filter
- Riddiford Lab (44) Apply Riddiford Lab filter
- Romani Lab (48) Apply Romani Lab filter
- Rubin Lab (146) Apply Rubin Lab filter
- Saalfeld Lab (64) Apply Saalfeld Lab filter
- Satou Lab (16) Apply Satou Lab filter
- Scheffer Lab (38) Apply Scheffer Lab filter
- Schreiter Lab (68) Apply Schreiter Lab filter
- Sgro Lab (21) Apply Sgro Lab filter
- Shroff Lab (31) Apply Shroff Lab filter
- Simpson Lab (23) Apply Simpson Lab filter
- Singer Lab (80) Apply Singer Lab filter
- Spruston Lab (94) Apply Spruston Lab filter
- Stern Lab (158) Apply Stern Lab filter
- Sternson Lab (54) Apply Sternson Lab filter
- Stringer Lab (39) Apply Stringer Lab filter
- Svoboda Lab (135) Apply Svoboda Lab filter
- Tebo Lab (34) Apply Tebo Lab filter
- Tervo Lab (9) Apply Tervo Lab filter
- Tillberg Lab (21) Apply Tillberg Lab filter
- Tjian Lab (64) Apply Tjian Lab filter
- Truman Lab (88) Apply Truman Lab filter
- Turaga Lab (52) Apply Turaga Lab filter
- Turner Lab (39) Apply Turner Lab filter
- Vale Lab (8) Apply Vale Lab filter
- Voigts Lab (3) Apply Voigts Lab filter
- Wang (Meng) Lab (23) Apply Wang (Meng) Lab filter
- Wang (Shaohe) Lab (25) Apply Wang (Shaohe) Lab filter
- Wu Lab (9) Apply Wu Lab filter
- Zlatic Lab (28) Apply Zlatic Lab filter
- Zuker Lab (25) Apply Zuker Lab filter
Associated Project Team
- CellMap (12) Apply CellMap filter
- COSEM (3) Apply COSEM filter
- FIB-SEM Technology (5) Apply FIB-SEM Technology filter
- Fly Descending Interneuron (12) Apply Fly Descending Interneuron filter
- Fly Functional Connectome (14) Apply Fly Functional Connectome filter
- Fly Olympiad (5) Apply Fly Olympiad filter
- FlyEM (56) Apply FlyEM filter
- FlyLight (50) Apply FlyLight filter
- GENIE (47) Apply GENIE filter
- Integrative Imaging (6) Apply Integrative Imaging filter
- Larval Olympiad (2) Apply Larval Olympiad filter
- MouseLight (18) Apply MouseLight filter
- NeuroSeq (1) Apply NeuroSeq filter
- ThalamoSeq (1) Apply ThalamoSeq filter
- Tool Translation Team (T3) (27) Apply Tool Translation Team (T3) filter
- Transcription Imaging (49) Apply Transcription Imaging filter
Publication Date
- 2025 (196) Apply 2025 filter
- 2024 (212) Apply 2024 filter
- 2023 (159) Apply 2023 filter
- 2022 (192) Apply 2022 filter
- 2021 (194) Apply 2021 filter
- 2020 (196) Apply 2020 filter
- 2019 (202) Apply 2019 filter
- 2018 (232) Apply 2018 filter
- 2017 (217) Apply 2017 filter
- 2016 (209) Apply 2016 filter
- 2015 (252) Apply 2015 filter
- 2014 (236) Apply 2014 filter
- 2013 (194) Apply 2013 filter
- 2012 (190) Apply 2012 filter
- 2011 (190) Apply 2011 filter
- 2010 (161) Apply 2010 filter
- 2009 (158) Apply 2009 filter
- 2008 (140) Apply 2008 filter
- 2007 (106) Apply 2007 filter
- 2006 (92) Apply 2006 filter
- 2005 (67) Apply 2005 filter
- 2004 (57) Apply 2004 filter
- 2003 (58) Apply 2003 filter
- 2002 (39) Apply 2002 filter
- 2001 (28) Apply 2001 filter
- 2000 (29) Apply 2000 filter
- 1999 (14) Apply 1999 filter
- 1998 (18) Apply 1998 filter
- 1997 (16) Apply 1997 filter
- 1996 (10) Apply 1996 filter
- 1995 (18) Apply 1995 filter
- 1994 (12) Apply 1994 filter
- 1993 (10) Apply 1993 filter
- 1992 (6) Apply 1992 filter
- 1991 (11) Apply 1991 filter
- 1990 (11) Apply 1990 filter
- 1989 (6) Apply 1989 filter
- 1988 (1) Apply 1988 filter
- 1987 (7) Apply 1987 filter
- 1986 (4) Apply 1986 filter
- 1985 (5) Apply 1985 filter
- 1984 (2) Apply 1984 filter
- 1983 (2) Apply 1983 filter
- 1982 (3) Apply 1982 filter
- 1981 (3) Apply 1981 filter
- 1980 (1) Apply 1980 filter
- 1979 (1) Apply 1979 filter
- 1976 (2) Apply 1976 filter
- 1973 (1) Apply 1973 filter
- 1970 (1) Apply 1970 filter
- 1967 (1) Apply 1967 filter
Type of Publication
4172 Publications
Showing 2611-2620 of 4172 resultsAnimals communicate using sounds in a wide range of contexts, and auditory systems must encode behaviorally relevant acoustic features to drive appropriate reactions. How feature detection emerges along auditory pathways has been difficult to solve due to challenges in mapping the underlying circuits and characterizing responses to behaviorally relevant features. Here, we study auditory activity in the Drosophila melanogaster brain and investigate feature selectivity for the two main modes of fly courtship song, sinusoids and pulse trains. We identify 24 new cell types of the intermediate layers of the auditory pathway, and using a new connectomic resource, FlyWire, we map all synaptic connections between these cell types, in addition to connections to known early and higher-order auditory neurons-this represents the first circuit-level map of the auditory pathway. We additionally determine the sign (excitatory or inhibitory) of most synapses in this auditory connectome. We find that auditory neurons display a continuum of preferences for courtship song modes and that neurons with different song-mode preferences and response timescales are highly interconnected in a network that lacks hierarchical structure. Nonetheless, we find that the response properties of individual cell types within the connectome are predictable from their inputs. Our study thus provides new insights into the organization of auditory coding within the Drosophila brain.
The stomatogastric ganglion (STG) of the crab Cancer productus contains approximately 30 neurons arrayed into two different networks (gastric mill and pyloric), each of which produces a distinct motor pattern in vitro. Here we show that the functional division of the STG into these two networks requires intact NO-cGMP signaling. Multiple nitric oxide synthase (NOS)-like proteins are expressed in the stomatogastric nervous system, and NO appears to be released as an orthograde transmitter from descending inputs to the STG. The receptor of NO, a soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC), is expressed in a subset of neurons in both motor networks. When NO diffusion or sGC activation are blocked within the ganglion, the two networks combine into a single conjoint circuit. The gastric mill motor rhythm breaks down, and several gastric neurons pattern switch and begin firing in pyloric time. The functional reorganization of the STG is both rapid and reversible, and the gastric mill motor rhythm is restored when the ganglion is returned to normal saline. Finally, pharmacological manipulations of the NO-cGMP pathway are ineffective when descending modulatory inputs to the STG are blocked. This suggests that the NO-cGMP pathway may interact with other biochemical cascades to partition rhythmic motor output from the ganglion.
BACKGROUND: During courtship, male Drosophila melanogaster sing a multipart courtship song to female flies. This song is of particular interest because (1) it is species specific and varies widely within the genus, (2) it is a gating stimulus for females, who are sensitive detectors of conspecific song, and (3) it is the only sexual signal that is under both neural and genetic control. This song is perceived via mechanosensory neurons in the antennal Johnston's organ, which innervate the antennal mechanosensory and motor center (AMMC) of the brain. However, AMMC outputs that are responsible for detection and discrimination of conspecific courtship song remain unknown. RESULTS: Using a large-scale anatomical screen of AMMC interneurons, we identify seven projection neurons (aPNs) and five local interneurons (aLNs) that outline a complex architecture for the ascending mechanosensory pathway. Neuronal inactivation and hyperactivation during behavior reveal that only two classes of interneurons are necessary for song responses--the projection neuron aPN1 and GABAergic interneuron aLN(al). These neurons are necessary in both male and female flies. Physiological recordings in aPN1 reveal the integration of courtship song as a function of pulse rate and outline an intracellular transfer function that likely facilitates the response to conspecific song. CONCLUSIONS: These results reveal a critical pathway for courtship hearing in male and female flies, in which both aLN(al) and aPN1 mediate the detection of conspecific song. The pathways arising from these neurons likely serve as a critical neural substrate for behavioral reproductive isolation in D. melanogaster.
Midbrain dopaminergic (DA) neurons are thought to guide learning via phasic elevations of firing in response to reward predicting stimuli. The mechanism for these signals remains unclear. Using extracellular recording during associative learning, we found that inhibitory neurons in the ventral midbrain of mice responded to salient auditory stimuli with a burst of activity that occurred before the onset of the phasic response of DA neurons. This population of inhibitory neurons exhibited enhanced responses during extinction and was anticorrelated with the phasic response of simultaneously recorded DA neurons. Optogenetic stimulation revealed that this population was, in part, derived from inhibitory projection neurons of the substantia nigra that provide a robust monosynaptic inhibition of DA neurons. Thus, our results elaborate on the dynamic upstream circuits that shape the phasic activity of DA neurons and suggest that the inhibitory microcircuit of the midbrain is critical for new learning in extinction.
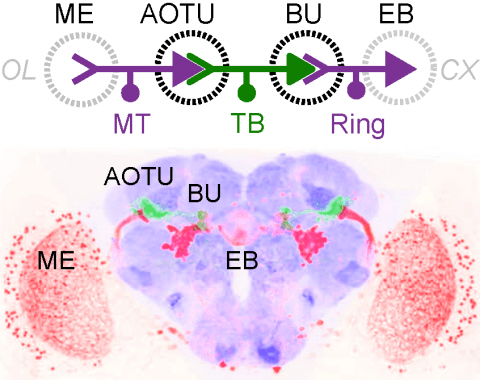
Many animals orient using visual cues, but how a single cue is selected from among many is poorly understood. Here we show that Drosophila ring neurons—central brain neurons implicated in navigation—display visual stimulus selection. Using in vivo two-color two-photon imaging with genetically encoded calcium indicators, we demonstrate that individual ring neurons inherit simple-cell-like receptive fields from their upstream partners. Stimuli in the contralateral visual field suppressed responses to ipsilateral stimuli in both populations. Suppression strength depended on when and where the contralateral stimulus was presented, an effect stronger in ring neurons than in their upstream inputs. This history-dependent effect on the temporal structure of visual responses, which was well modeled by a simple biphasic filter, may determine how visual references are selected for the fly's internal compass. Our approach highlights how two-color calcium imaging can help identify and localize the origins of sensory transformations across synaptically connected neural populations.
Metazoans detect and differentiate between innocuous (non-painful) and/or noxious (harmful) environmental cues using primary sensory neurons, which serve as the first node in a neural network that computes stimulus-specific behaviors to either navigate away from injury-causing conditions or to perform protective behaviors that mitigate extensive injury. The ability of an animal to detect and respond to various sensory stimuli depends upon molecular diversity in the primary sensors and the underlying neural circuitry responsible for the relevant behavioral action selection. Recent studies in Drosophila larvae have revealed that somatosensory class III multidendritic (CIII md) neurons function as multimodal sensors regulating distinct behavioral responses to innocuous mechanical and nociceptive thermal stimuli. Recent advances in circuit bases of behavior have identified and functionally validated \Drosophila larval somatosensory circuitry involved in innocuous (mechanical) and noxious (heat and mechanical) cues. However, central processing of cold nociceptive cues remained unexplored. We implicate multisensory integrators (Basins), premotor (Down-and-Back), and projection (A09e and TePns) neurons as neural substrates required for cold-evoked behavioral and calcium responses. Neural silencing of cell types downstream of CIII md neurons led to significant reductions in cold-evoked behaviors, and neural co-activation of CIII md neurons plus additional cell types facilitated larval contraction (CT) responses. Further, we demonstrate that optogenetic activation of CIII md neurons evokes calcium increases in these neurons. Finally, we characterize the premotor to motor neuron network underlying cold-evoked CT and delineate the muscular basis of CT response. Collectively, we demonstrate how Drosophila larvae process cold stimuli through functionally diverse somatosensory circuitry responsible for generating stimulus-specific behaviors.
Animals use sensory information to move toward more favorable conditions. Drosophila larvae can move up or down gradients of odors (chemotax), light (phototax), and temperature (thermotax) by modulating the probability, direction, and size of turns based on sensory input. Whether larvae can anemotax in gradients of mechanosensory cues is unknown. Further, although many of the sensory neurons that mediate taxis have been described, the central circuits are not well understood. Here, we used high-throughput, quantitative behavioral assays to demonstrate Drosophila larvae anemotax in gradients of wind speeds and to characterize the behavioral strategies involved. We found that larvae modulate the probability, direction, and size of turns to move away from higher wind speeds. This suggests that similar central decision-making mechanisms underlie taxis in somatosensory and other sensory modalities. By silencing the activity of single or very few neuron types in a behavioral screen, we found two sensory (chordotonal and multidendritic class III) and six nerve cord neuron types involved in anemotaxis. We reconstructed the identified neurons in an electron microscopy volume that spans the entire larval nervous system and found they received direct input from the mechanosensory neurons or from each other. In this way, we identified local interneurons and first- and second-order subesophageal zone (SEZ) and brain projection neurons. Finally, silencing a dopaminergic brain neuron type impairs anemotaxis. These findings suggest that anemotaxis involves both nerve cord and brain circuits. The candidate neurons and circuitry identified in our study provide a basis for future detailed mechanistic understanding of the circuit principles of anemotaxis.
Small animals navigate in the environment as a function of varying sensory information in order to reach more favorable environmental conditions. To achieve this Drosophila larvae alternate periods of runs and turns in gradients of light, temperature, odors and CO2. While the sensory neurons that mediate the navigation behaviors in the different sensory gradients have been described, where and how are these navigational strategies are implemented in the central nervous system and controlled by neuronal circuit elements is not well known. Here we characterize for the first time the navigational strategies of Drosophila larvae in gradients of air-current speeds using high-throughput behavioral assays and quantitative behavioral analysis. We find that larvae extend runs when facing favorable conditions and increase turn rate when facing unfavorable direction, a strategy they use in other sensory modalities as well. By silencing the activity of individual neurons and very sparse expression patterns (2 or 3 neuron types), we further identify the sensory neurons and circuit elements in the ventral nerve cord and brain of the larva required for navigational decisions during anemotaxis. The phenotypes of these central neurons are consistent with a mechanism where the increase of the turning rate in unfavorable conditions and decrease in turning rate in favorable conditions are independently controlled.
As observed in human language learning and song learning in birds, the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster changes its auditory behaviors according to prior sound experiences. This phenomenon, known as song preference learning in flies, requires GABAergic input to pC1 neurons in the brain, with these neurons playing a key role in mating behavior. The neural circuit basis of this GABAergic input, however, is not known. Here, we find that GABAergic neurons expressing the sex-determination gene doublesex are necessary for song preference learning. In the brain, only four doublesex-expressing GABAergic neurons exist per hemibrain, identified as pCd-2 neurons. pCd-2 neurons directly, and in many cases mutually, connect with pC1 neurons, suggesting the existence of reciprocal circuits between them. Moreover, GABAergic and dopaminergic inputs to doublesex-expressing GABAergic neurons are necessary for song preference learning. Together, this study provides a neural circuit model that underlies experience-dependent auditory plasticity at a single-cell resolution.
Insects exhibit an elaborate repertoire of behaviors in response to environmental stimuli. The central complex plays a key role in combining various modalities of sensory information with an insect's internal state and past experience to select appropriate responses. Progress has been made in understanding the broad spectrum of outputs from the central complex neuropils and circuits involved in numerous behaviors. Many resident neurons have also been identified. However, the specific roles of these intricate structures and the functional connections between them remain largely obscure. Significant gains rely on obtaining a comprehensive catalog of the neurons and associated GAL4 lines that arborize within these brain regions, and on mapping neuronal pathways connecting these structures. To this end, small populations of neurons in the Drosophila melanogaster central complex were stochastically labeled using the multicolor flip-out technique and a catalog was created of the neurons, their morphologies, trajectories, relative arrangements, and corresponding GAL4 lines. This report focuses on one structure of the central complex, the protocerebral bridge, and identifies just 17 morphologically distinct cell types that arborize in this structure. This work also provides new insights into the anatomical structure of the four components of the central complex and its accessory neuropils. Most strikingly, we found that the protocerebral bridge contains 18 glomeruli, not 16, as previously believed. Revised wiring diagrams that take into account this updated architectural design are presented. This updated map of the Drosophila central complex will facilitate a deeper behavioral and physiological dissection of this sophisticated set of structures. J. Comp. Neurol. 523:997-1037, 2015. © 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.