Filter
Associated Lab
- Aguilera Castrejon Lab (17) Apply Aguilera Castrejon Lab filter
- Ahrens Lab (68) Apply Ahrens Lab filter
- Aso Lab (42) Apply Aso Lab filter
- Baker Lab (38) Apply Baker Lab filter
- Betzig Lab (115) Apply Betzig Lab filter
- Beyene Lab (14) Apply Beyene Lab filter
- Bock Lab (17) Apply Bock Lab filter
- Branson Lab (54) Apply Branson Lab filter
- Card Lab (43) Apply Card Lab filter
- Cardona Lab (64) Apply Cardona Lab filter
- Chklovskii Lab (13) Apply Chklovskii Lab filter
- Clapham Lab (15) Apply Clapham Lab filter
- Cui Lab (19) Apply Cui Lab filter
- Darshan Lab (12) Apply Darshan Lab filter
- Dennis Lab (1) Apply Dennis Lab filter
- Dickson Lab (46) Apply Dickson Lab filter
- Druckmann Lab (25) Apply Druckmann Lab filter
- Dudman Lab (52) Apply Dudman Lab filter
- Eddy/Rivas Lab (30) Apply Eddy/Rivas Lab filter
- Egnor Lab (11) Apply Egnor Lab filter
- Espinosa Medina Lab (21) Apply Espinosa Medina Lab filter
- Feliciano Lab (10) Apply Feliciano Lab filter
- Fetter Lab (41) Apply Fetter Lab filter
- FIB-SEM Technology (1) Apply FIB-SEM Technology filter
- Fitzgerald Lab (29) Apply Fitzgerald Lab filter
- Freeman Lab (15) Apply Freeman Lab filter
- Funke Lab (41) Apply Funke Lab filter
- Gonen Lab (91) Apply Gonen Lab filter
- Grigorieff Lab (62) Apply Grigorieff Lab filter
- Harris Lab (64) Apply Harris Lab filter
- Heberlein Lab (94) Apply Heberlein Lab filter
- Hermundstad Lab (29) Apply Hermundstad Lab filter
- Hess Lab (79) Apply Hess Lab filter
- Ilanges Lab (2) Apply Ilanges Lab filter
- Jayaraman Lab (47) Apply Jayaraman Lab filter
- Ji Lab (33) Apply Ji Lab filter
- Johnson Lab (6) Apply Johnson Lab filter
- Kainmueller Lab (19) Apply Kainmueller Lab filter
- Karpova Lab (14) Apply Karpova Lab filter
- Keleman Lab (13) Apply Keleman Lab filter
- Keller Lab (76) Apply Keller Lab filter
- Koay Lab (18) Apply Koay Lab filter
- Lavis Lab (154) Apply Lavis Lab filter
- Lee (Albert) Lab (34) Apply Lee (Albert) Lab filter
- Leonardo Lab (23) Apply Leonardo Lab filter
- Li Lab (30) Apply Li Lab filter
- Lippincott-Schwartz Lab (178) Apply Lippincott-Schwartz Lab filter
- Liu (Yin) Lab (7) Apply Liu (Yin) Lab filter
- Liu (Zhe) Lab (64) Apply Liu (Zhe) Lab filter
- Looger Lab (138) Apply Looger Lab filter
- Magee Lab (49) Apply Magee Lab filter
- Menon Lab (18) Apply Menon Lab filter
- Murphy Lab (13) Apply Murphy Lab filter
- O'Shea Lab (7) Apply O'Shea Lab filter
- Otopalik Lab (13) Apply Otopalik Lab filter
- Pachitariu Lab (49) Apply Pachitariu Lab filter
- Pastalkova Lab (18) Apply Pastalkova Lab filter
- Pavlopoulos Lab (19) Apply Pavlopoulos Lab filter
- Pedram Lab (15) Apply Pedram Lab filter
- Podgorski Lab (16) Apply Podgorski Lab filter
- Reiser Lab (53) Apply Reiser Lab filter
- Riddiford Lab (44) Apply Riddiford Lab filter
- Romani Lab (48) Apply Romani Lab filter
- Rubin Lab (147) Apply Rubin Lab filter
- Saalfeld Lab (64) Apply Saalfeld Lab filter
- Satou Lab (16) Apply Satou Lab filter
- Scheffer Lab (38) Apply Scheffer Lab filter
- Schreiter Lab (68) Apply Schreiter Lab filter
- Sgro Lab (21) Apply Sgro Lab filter
- Shroff Lab (31) Apply Shroff Lab filter
- Simpson Lab (23) Apply Simpson Lab filter
- Singer Lab (80) Apply Singer Lab filter
- Spruston Lab (97) Apply Spruston Lab filter
- Stern Lab (158) Apply Stern Lab filter
- Sternson Lab (54) Apply Sternson Lab filter
- Stringer Lab (39) Apply Stringer Lab filter
- Svoboda Lab (135) Apply Svoboda Lab filter
- Tebo Lab (35) Apply Tebo Lab filter
- Tervo Lab (9) Apply Tervo Lab filter
- Tillberg Lab (21) Apply Tillberg Lab filter
- Tjian Lab (64) Apply Tjian Lab filter
- Truman Lab (88) Apply Truman Lab filter
- Turaga Lab (53) Apply Turaga Lab filter
- Turner Lab (39) Apply Turner Lab filter
- Vale Lab (8) Apply Vale Lab filter
- Voigts Lab (3) Apply Voigts Lab filter
- Wang (Meng) Lab (27) Apply Wang (Meng) Lab filter
- Wang (Shaohe) Lab (25) Apply Wang (Shaohe) Lab filter
- Wu Lab (9) Apply Wu Lab filter
- Zlatic Lab (28) Apply Zlatic Lab filter
- Zuker Lab (25) Apply Zuker Lab filter
Associated Project Team
- CellMap (12) Apply CellMap filter
- COSEM (3) Apply COSEM filter
- FIB-SEM Technology (5) Apply FIB-SEM Technology filter
- Fly Descending Interneuron (12) Apply Fly Descending Interneuron filter
- Fly Functional Connectome (14) Apply Fly Functional Connectome filter
- Fly Olympiad (5) Apply Fly Olympiad filter
- FlyEM (56) Apply FlyEM filter
- FlyLight (50) Apply FlyLight filter
- GENIE (47) Apply GENIE filter
- Integrative Imaging (7) Apply Integrative Imaging filter
- Larval Olympiad (2) Apply Larval Olympiad filter
- MouseLight (18) Apply MouseLight filter
- NeuroSeq (1) Apply NeuroSeq filter
- ThalamoSeq (1) Apply ThalamoSeq filter
- Tool Translation Team (T3) (28) Apply Tool Translation Team (T3) filter
- Transcription Imaging (49) Apply Transcription Imaging filter
Publication Date
- 2025 (215) Apply 2025 filter
- 2024 (212) Apply 2024 filter
- 2023 (158) Apply 2023 filter
- 2022 (192) Apply 2022 filter
- 2021 (194) Apply 2021 filter
- 2020 (196) Apply 2020 filter
- 2019 (202) Apply 2019 filter
- 2018 (232) Apply 2018 filter
- 2017 (217) Apply 2017 filter
- 2016 (209) Apply 2016 filter
- 2015 (252) Apply 2015 filter
- 2014 (236) Apply 2014 filter
- 2013 (194) Apply 2013 filter
- 2012 (190) Apply 2012 filter
- 2011 (190) Apply 2011 filter
- 2010 (161) Apply 2010 filter
- 2009 (158) Apply 2009 filter
- 2008 (140) Apply 2008 filter
- 2007 (106) Apply 2007 filter
- 2006 (92) Apply 2006 filter
- 2005 (67) Apply 2005 filter
- 2004 (57) Apply 2004 filter
- 2003 (58) Apply 2003 filter
- 2002 (39) Apply 2002 filter
- 2001 (28) Apply 2001 filter
- 2000 (29) Apply 2000 filter
- 1999 (14) Apply 1999 filter
- 1998 (18) Apply 1998 filter
- 1997 (16) Apply 1997 filter
- 1996 (10) Apply 1996 filter
- 1995 (18) Apply 1995 filter
- 1994 (12) Apply 1994 filter
- 1993 (10) Apply 1993 filter
- 1992 (6) Apply 1992 filter
- 1991 (11) Apply 1991 filter
- 1990 (11) Apply 1990 filter
- 1989 (6) Apply 1989 filter
- 1988 (1) Apply 1988 filter
- 1987 (7) Apply 1987 filter
- 1986 (4) Apply 1986 filter
- 1985 (5) Apply 1985 filter
- 1984 (2) Apply 1984 filter
- 1983 (2) Apply 1983 filter
- 1982 (3) Apply 1982 filter
- 1981 (3) Apply 1981 filter
- 1980 (1) Apply 1980 filter
- 1979 (1) Apply 1979 filter
- 1976 (2) Apply 1976 filter
- 1973 (1) Apply 1973 filter
- 1970 (1) Apply 1970 filter
- 1967 (1) Apply 1967 filter
Type of Publication
4190 Publications
Showing 3741-3750 of 4190 resultsFunctional imaging using fluorescent indicators has revolutionized biology, but additional sensor scaffolds are needed to access properties such as bright, far-red emission. Here, we introduce a new platform for 'chemigenetic' fluorescent indicators, utilizing the self-labeling HaloTag protein conjugated to environmentally sensitive synthetic fluorophores. We solve a crystal structure of HaloTag bound to a rhodamine dye ligand to guide engineering efforts to modulate the dye environment. We show that fusion of HaloTag with protein sensor domains that undergo conformational changes near the bound dye results in large and rapid changes in fluorescence output. This generalizable approach affords bright, far-red calcium and voltage sensors with highly tunable photophysical and chemical properties, which can reliably detect single action potentials in cultured neurons.
Repeated alcohol consumption leads to the development of tolerance, simply defined as an acquired resistance to the physiological and behavioural effects of the drug. This tolerance allows increased alcohol consumption, which over time leads to physical dependence and possibly addiction. Previous studies have shown that Drosophila develop ethanol tolerance, with kinetics of acquisition and dissipation that mimic those seen in mammals. This tolerance requires the catecholamine octopamine, the functional analogue of mammalian noradrenaline. Here we describe a new gene, hangover, which is required for normal development of ethanol tolerance. hangover flies are also defective in responses to environmental stressors, such as heat and the free-radical-generating agent paraquat. Using genetic epistasis tests, we show that ethanol tolerance in Drosophila relies on two distinct molecular pathways: a cellular stress pathway defined by hangover, and a parallel pathway requiring octopamine. hangover encodes a large nuclear zinc-finger protein, suggesting a role in nucleic acid binding. There is growing recognition that stress, at both the cellular and systemic levels, contributes to drug- and addiction-related behaviours in mammals. Our studies suggest that this role may be conserved across evolution.
Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HB-EGF) is a ligand for EGF receptor (EGFR) and possesses the ability to signal in juxtacrine, autocrine and/or paracrine mode, with these alternatives being governed by the degree of proteolytic release of the ligand. Although the spatial range of diffusion of released HB-EGF is restricted by binding heparan-sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) in the extracellular matrix and/or cellular glycocalyx, ascertaining mechanisms governing non-released HB-EGF localization is also important for understanding its effects. We have employed a new method for independently tracking the localization of the extracellular EGF-like domain of HB-EGF and the cytoplasmic C-terminus. A striking observation was the absence of the HB-EGF transmembrane pro-form from the leading edge of COS-7 cells in a wound-closure assay; instead, this protein localized in regions of cell-cell contact. A battery of detailed experiments found that this localization derives from a trans interaction between extracellular HSPGs and the HB-EGF heparin-binding domain, and that disruption of this interaction leads to increased release of soluble ligand and a switch in cell phenotype from juxtacrine-induced growth inhibition to autocrine-induced proliferation. Our results indicate that extracellular HSPGs serve to sequester the transmembrane pro-form of HB-EGF at the point of cell-cell contact, and that this plays a role in governing the balance between juxtacrine versus autocrine and paracrine signaling.
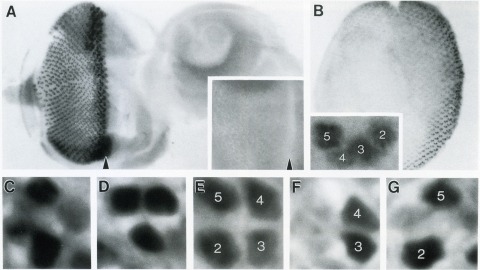
The Drosophila homeo box gene rough is required in photoreceptor cells R2 and R5 for normal eye development. We show here that rough protein expression is limited to a subset of cells in the developing retina where it is transiently expressed for 30-60 hr. The rough protein is first expressed broadly in the morphogenetic furrow but is rapidly restricted to the R2, R3, R4, and R5 precursor cells. Ubiquitous expression of rough under the control of the hsp70 promoter in third-instar larvae suppresses the initial steps of ommatidial assembly. Structures derived from other imaginal discs are not affected. Ectopic expression of rough in the R7 precursor, through the use of the sevenless promoter, causes this cell to develop into an R1-6 photoreceptor subtype; however, this cell still requires sevenless function for its neural differentiation. Taken together with previous analyses of the rough mutant phenotype, these results suggest that the normal role of rough is to establish the unique cell identity of photoreceptors R2 and R5.
The developmental mechanisms that regulate the relative size and shape of organs have remained obscure despite almost a century of interest in the problem and the fact that changes in relative size represent the dominant mode of evolutionary change. Here, I investigate how the Hox gene Ultrabithorax (Ubx) instructs the legs on the third thoracic segment of Drosophila melanogaster to develop with a different size and shape from the legs on the second thoracic segment. Through loss-of-function and gain-of-function experiments, I demonstrate that different segments of the leg, the femur and the first tarsal segment, and even different regions of the femur, regulate their size in response to Ubx expression through qualitatively different mechanisms. In some regions, Ubx acts autonomously to specify shape and size, whereas in other regions, Ubx influences size through nonautonomous mechanisms. Loss of Ubx autonomously reduces cell size in the T3 femur, but this reduction seems to be partially compensated by an increase in cell numbers, so that it is unclear what effect cell size and number directly have on femur size. Loss of Ubx has both autonomous and nonautonomous effects on cell number in different regions of the basitarsus, but again there is not a strong correlation between cell size or number and organ size. Total organ size appears to be regulated through mechanisms that operate at the level of the entire leg segment (femur or basitarsus) relatively independently of the behavior of individual subpopulations of cells within the segment.
In contrast to our increasingly detailed understanding of how synaptic plasticity provides a cellular substrate for learning and memory, it is less clear how a neuron’s voltage-gated ion channels interact with plastic changes in synaptic strength to influence behavior. We find, using generalized and regional knockout mice, that deletion of the HCN1 channel causes profound motor learning and memory deficits in swimming and rotarod tasks. In cerebellar Purkinje cells, which are a key component of the cerebellar circuit for learning of correctly timed movements, HCN1 mediates an inward current that stabilizes the integrative properties of Purkinje cells and ensures that their input-output function is independent of the previous history of their activity. We suggest that this nonsynaptic integrative function of HCN1 is required for accurate decoding of input patterns and thereby enables synaptic plasticity to appropriately influence the performance of motor activity.
A surprising finding of recent studies in mouse is the dominance of widespread movement-related activity throughout the brain, including in early sensory areas. In awake subjects, failing to account for movement risks misattributing movement-related activity to other (e.g., sensory or cognitive) processes. In this article, we 1) review task designs for separating task-related and movement-related activity, 2) review three 'case studies' in which not considering movement would have resulted in critically different interpretations of neuronal function, and 3) discuss functional couplings that may prevent us from ever fully isolating sensory, motor, and cognitive-related activity. Our main thesis is that neural signals related to movement are ubiquitous, and therefore ought to be considered first and foremost when attempting to correlate neuronal activity with task-related processes.
Voltage-gated ion channels are responsible for transmitting electrochemical signals in both excitable and non-excitable cells. Structural studies of voltage-gated potassium and sodium channels by X-ray crystallography have revealed atomic details on their voltage-sensor domains (VSDs) and pore domains, and were put in context of disparate mechanistic views on the voltage-driven conformational changes in these proteins. Functional investigation of voltage-gated channels in membranes, however, showcased a mechanism of lipid-dependent gating for voltage-gated channels, suggesting that the lipids play an indispensible and critical role in the proper gating of many of these channels. Structure determination of membrane-embedded voltage-gated ion channels appears to be the next frontier in fully addressing the mechanism by which the VSDs control channel opening. Currently electron crystallography is the only structural biology method in which a membrane protein of interest is crystallized within a complete lipid-bilayer mimicking the native environment of a biological membrane. At a sufficiently high resolution, an electron crystallographic structure could reveal lipids, the channel and their mutual interactions at the atomic level. Electron crystallography is therefore a promising avenue toward understanding how lipids modulate channel activation through close association with the VSDs.
The manner in which different distributions of synaptic weights onto cortical neurons shape their spiking activity remains open. To characterize a homogeneous neuronal population, we use the master equation for generalized leaky integrate-and-fire neurons with shot-noise synapses. We develop fast semi-analytic numerical methods to solve this equation for either current or conductance synapses, with and without synaptic depression. We show that its solutions match simulations of equivalent neuronal networks better than those of the Fokker-Planck equation and we compute bounds on the network response to non-instantaneous synapses. We apply these methods to study different synaptic weight distributions in feed-forward networks. We characterize the synaptic amplitude distributions using a set of measures, called tail weight numbers, designed to quantify the preponderance of very strong synapses. Even if synaptic amplitude distributions are equated for both the total current and average synaptic weight, distributions with sparse but strong synapses produce higher responses for small inputs, leading to a larger operating range. Furthermore, despite their small number, such synapses enable the network to respond faster and with more stability in the face of external fluctuations.
Dysfunction of the basal ganglia produces severe deficits in the timing, initiation, and vigor of movement. These diverse impairments suggest a control system gone awry. In engineered systems, feedback is critical for control. By contrast, models of the basal ganglia highlight feedforward circuitry and ignore intrinsic feedback circuits. In this study, we show that feedback via axon collaterals of substantia nigra projection neurons control the gain of the basal ganglia output. Through a combination of physiology, optogenetics, anatomy, and circuit mapping, we elaborate a general circuit mechanism for gain control in a microcircuit lacking interneurons. Our data suggest that diverse tonic firing rates, weak unitary connections and a spatially diffuse collateral circuit with distinct topography and kinetics from feedforward input is sufficient to implement divisive feedback inhibition. The importance of feedback for engineered systems implies that the intranigral microcircuit, despite its absence from canonical models, could be essential to basal ganglia function. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.02397.001.