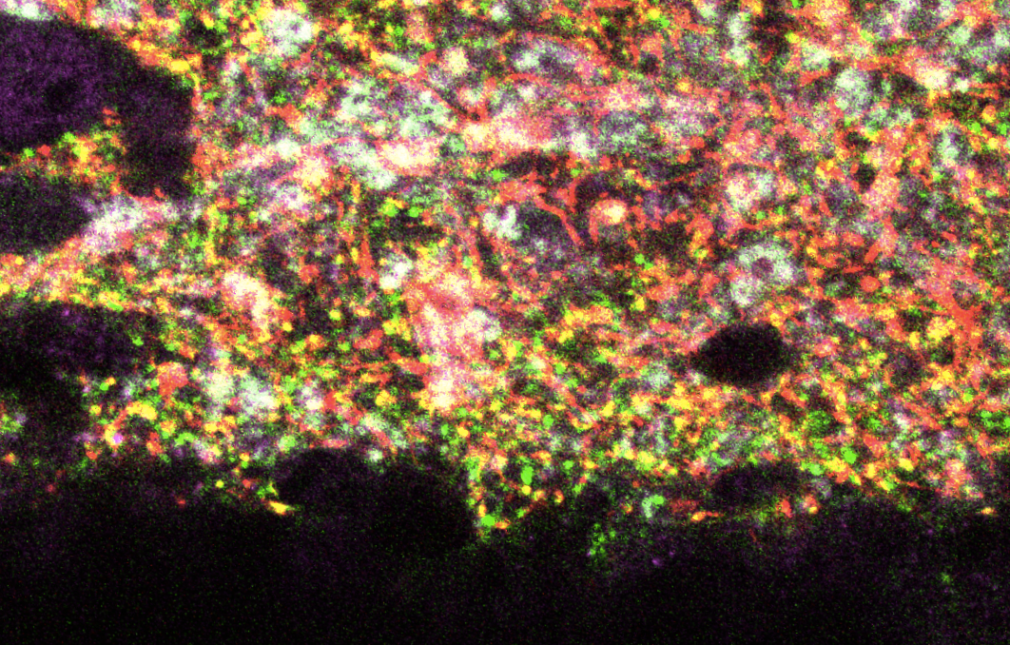
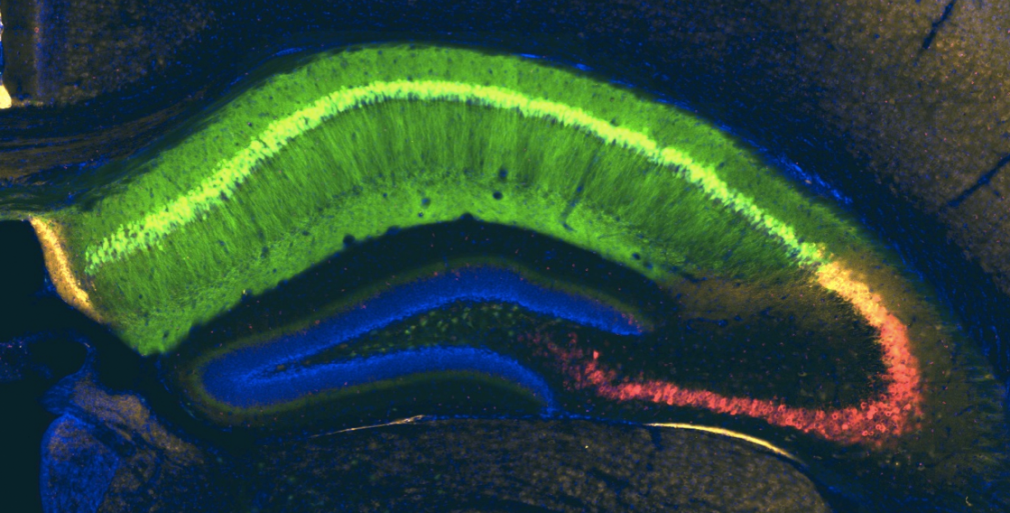
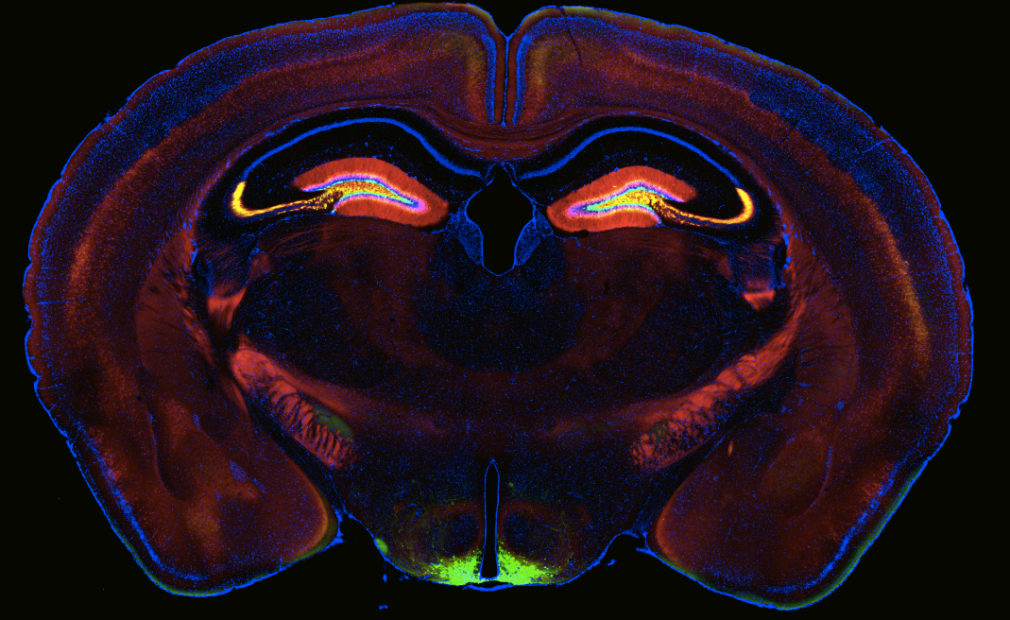
We and others have identified heterogeneity in the population of pyramidal neurons projecting out of the hippocampus (Mizuseki et al., 2011; Graves et al., 2012). Physiological methods, while powerful for interrogating functional properties, are relatively low throughput, therefore making it difficult to determine the cell types comprising a circuit systematically and completely. By comparison, analysis of the Allen Brain Atlas in situ hybridization data (Lein et al., 2007) has led to a more comprehensive picture of the heterogeneity of gene expression in the hippocampus (Thompson et al., 2008; Dong et al., 2009). A drawback of this approach, however, is the difficulty in assigning gene expression to a particular cell type or to return reliably to the same cells for comparative analysis of gene expression and function.
To address these problems, Mark Cembrowski (with help from many others at Janelia) is performing a hippocampus-wide screen of gene expression in genetically and anatomically defined cell types using next-generation RNA sequencing.
Using a variety of mouse lines expressing Cre-recombinase (see gallery below), genetically defined cells are induced to express fluorescent reporter proteins using a variety of approaches. Cells of interest are then microdissected and sorted for subsequent RNA library preparation and sequencing (Hempel et al., 2007).
The results of this screen will be used for a variety of purposes, including identification of marker genes for cell types, comparison of gene expression across cell types, and analysis of gene ontology to infer function.
Mark Cembrowski has received assistance on this project from many people at Janelia, including: Julia Bachman, Andrew Lemire, Brenda Shields, Ken Sugino, and Lihua Wang.
References
Dong, HW, Swanson, LW, Chen, L, Fanselow, MS, and Toga, AW. Genomic-anatomic evidence for distinct functional domains in hippocampal field CA1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. 106:11794-99, 2009.
Graves AR, Moore SJ, Bloss EB, Mensh BD, Kath WL, Spruston N. Hippocampal pyramidal neurons comprise two distinct cell types that are countermodulated by metabotropic receptors. Neuron 76:776-89, 2012.
Hempel CM, Sugino K, Nelson SB. A manual method for the purification of fluorescently labeled neurons from the mammalian brain. Nature Protocols 2:2924-29, 2007.
Lein ES, Hawrylycz MJ, Ao N, Ayres M, Bensinger A, Bernard A, Boe AF, Boguski MS, Brockway KS, Byrnes EJ, et al. Genome-wide atlas of gene expression in the adult mouse brain. Nature 445:168-76, 2007.
Mizuseki K, Diba K, Pastalkova E, Buzsaki G. Hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells form functionally distinct sublayers. Nature Neuroscience 14:1174-81, 2011.
Thompson CL, Pathak SD, Jeromin A, Ng LL, MacPherson CR, Mortrud MT, Cusick A, Riley ZL, Sunkin SM, Bernard A, et al. Genomic anatomy of the hippocampus. Neuron 60:1010-21, 2008.
Further reading
Bernard A, Sorensen SA, Lein, ES. Shifting the paradigm: new approaches for characterizing and classifying neurons. Current Opinion in Neurobiology 19:530-536, 2009.
Shin J, Ming GL, Song H. Decoding neural transcriptomes and epigenomes via high-throughput sequencing. Nature Neuroscience 17:1463-75, 2014.