Filter
Associated Lab
- Aguilera Castrejon Lab (2) Apply Aguilera Castrejon Lab filter
- Ahrens Lab (58) Apply Ahrens Lab filter
- Aso Lab (42) Apply Aso Lab filter
- Baker Lab (19) Apply Baker Lab filter
- Betzig Lab (103) Apply Betzig Lab filter
- Beyene Lab (10) Apply Beyene Lab filter
- Bock Lab (14) Apply Bock Lab filter
- Branson Lab (51) Apply Branson Lab filter
- Card Lab (37) Apply Card Lab filter
- Cardona Lab (45) Apply Cardona Lab filter
- Chklovskii Lab (10) Apply Chklovskii Lab filter
- Clapham Lab (14) Apply Clapham Lab filter
- Cui Lab (19) Apply Cui Lab filter
- Darshan Lab (8) Apply Darshan Lab filter
- Dennis Lab (1) Apply Dennis Lab filter
- Dickson Lab (32) Apply Dickson Lab filter
- Druckmann Lab (21) Apply Druckmann Lab filter
- Dudman Lab (41) Apply Dudman Lab filter
- Eddy/Rivas Lab (30) Apply Eddy/Rivas Lab filter
- Egnor Lab (4) Apply Egnor Lab filter
- Espinosa Medina Lab (18) Apply Espinosa Medina Lab filter
- Feliciano Lab (10) Apply Feliciano Lab filter
- Fetter Lab (31) Apply Fetter Lab filter
- FIB-SEM Technology (1) Apply FIB-SEM Technology filter
- Fitzgerald Lab (16) Apply Fitzgerald Lab filter
- Freeman Lab (15) Apply Freeman Lab filter
- Funke Lab (42) Apply Funke Lab filter
- Gonen Lab (59) Apply Gonen Lab filter
- Grigorieff Lab (34) Apply Grigorieff Lab filter
- Harris Lab (55) Apply Harris Lab filter
- Heberlein Lab (13) Apply Heberlein Lab filter
- Hermundstad Lab (26) Apply Hermundstad Lab filter
- Hess Lab (76) Apply Hess Lab filter
- Ilanges Lab (3) Apply Ilanges Lab filter
- Jayaraman Lab (44) Apply Jayaraman Lab filter
- Ji Lab (33) Apply Ji Lab filter
- Johnson Lab (1) Apply Johnson Lab filter
- Karpova Lab (13) Apply Karpova Lab filter
- Keleman Lab (8) Apply Keleman Lab filter
- Keller Lab (61) Apply Keller Lab filter
- Koay Lab (3) Apply Koay Lab filter
- Lavis Lab (144) Apply Lavis Lab filter
- Lee (Albert) Lab (29) Apply Lee (Albert) Lab filter
- Leonardo Lab (19) Apply Leonardo Lab filter
- Li Lab (6) Apply Li Lab filter
- Lippincott-Schwartz Lab (107) Apply Lippincott-Schwartz Lab filter
- Liu (Yin) Lab (2) Apply Liu (Yin) Lab filter
- Liu (Zhe) Lab (59) Apply Liu (Zhe) Lab filter
- Looger Lab (137) Apply Looger Lab filter
- Magee Lab (31) Apply Magee Lab filter
- Menon Lab (12) Apply Menon Lab filter
- Murphy Lab (6) Apply Murphy Lab filter
- O'Shea Lab (6) Apply O'Shea Lab filter
- Otopalik Lab (1) Apply Otopalik Lab filter
- Pachitariu Lab (39) Apply Pachitariu Lab filter
- Pastalkova Lab (5) Apply Pastalkova Lab filter
- Pavlopoulos Lab (7) Apply Pavlopoulos Lab filter
- Pedram Lab (4) Apply Pedram Lab filter
- Podgorski Lab (16) Apply Podgorski Lab filter
- Reiser Lab (49) Apply Reiser Lab filter
- Riddiford Lab (20) Apply Riddiford Lab filter
- Romani Lab (39) Apply Romani Lab filter
- Rubin Lab (110) Apply Rubin Lab filter
- Saalfeld Lab (47) Apply Saalfeld Lab filter
- Satou Lab (1) Apply Satou Lab filter
- Scheffer Lab (38) Apply Scheffer Lab filter
- Schreiter Lab (52) Apply Schreiter Lab filter
- Sgro Lab (2) Apply Sgro Lab filter
- Shroff Lab (31) Apply Shroff Lab filter
- Simpson Lab (18) Apply Simpson Lab filter
- Singer Lab (37) Apply Singer Lab filter
- Spruston Lab (61) Apply Spruston Lab filter
- Stern Lab (75) Apply Stern Lab filter
- Sternson Lab (47) Apply Sternson Lab filter
- Stringer Lab (36) Apply Stringer Lab filter
- Svoboda Lab (132) Apply Svoboda Lab filter
- Tebo Lab (11) Apply Tebo Lab filter
- Tervo Lab (9) Apply Tervo Lab filter
- Tillberg Lab (18) Apply Tillberg Lab filter
- Tjian Lab (17) Apply Tjian Lab filter
- Truman Lab (58) Apply Truman Lab filter
- Turaga Lab (41) Apply Turaga Lab filter
- Turner Lab (27) Apply Turner Lab filter
- Vale Lab (8) Apply Vale Lab filter
- Voigts Lab (4) Apply Voigts Lab filter
- Wang (Meng) Lab (27) Apply Wang (Meng) Lab filter
- Wang (Shaohe) Lab (6) Apply Wang (Shaohe) Lab filter
- Wong-Campos Lab (1) Apply Wong-Campos Lab filter
- Wu Lab (8) Apply Wu Lab filter
- Zlatic Lab (26) Apply Zlatic Lab filter
- Zuker Lab (5) Apply Zuker Lab filter
Associated Project Team
- CellMap (12) Apply CellMap filter
- COSEM (3) Apply COSEM filter
- FIB-SEM Technology (5) Apply FIB-SEM Technology filter
- Fly Descending Interneuron (12) Apply Fly Descending Interneuron filter
- Fly Functional Connectome (14) Apply Fly Functional Connectome filter
- Fly Olympiad (5) Apply Fly Olympiad filter
- FlyEM (56) Apply FlyEM filter
- FlyLight (50) Apply FlyLight filter
- GENIE (47) Apply GENIE filter
- Integrative Imaging (9) Apply Integrative Imaging filter
- Larval Olympiad (2) Apply Larval Olympiad filter
- MouseLight (18) Apply MouseLight filter
- NeuroSeq (1) Apply NeuroSeq filter
- ThalamoSeq (1) Apply ThalamoSeq filter
- Tool Translation Team (T3) (29) Apply Tool Translation Team (T3) filter
- Transcription Imaging (45) Apply Transcription Imaging filter
Associated Support Team
- Project Pipeline Support (5) Apply Project Pipeline Support filter
- Anatomy and Histology (18) Apply Anatomy and Histology filter
- Cryo-Electron Microscopy (41) Apply Cryo-Electron Microscopy filter
- Electron Microscopy (18) Apply Electron Microscopy filter
- Gene Targeting and Transgenics (11) Apply Gene Targeting and Transgenics filter
- High Performance Computing (7) Apply High Performance Computing filter
- Integrative Imaging (18) Apply Integrative Imaging filter
- Invertebrate Shared Resource (40) Apply Invertebrate Shared Resource filter
- Janelia Experimental Technology (37) Apply Janelia Experimental Technology filter
- Management Team (1) Apply Management Team filter
- Mass Spectrometry (1) Apply Mass Spectrometry filter
- Molecular Genomics (15) Apply Molecular Genomics filter
- Primary & iPS Cell Culture (14) Apply Primary & iPS Cell Culture filter
- Project Technical Resources (53) Apply Project Technical Resources filter
- Quantitative Genomics (20) Apply Quantitative Genomics filter
- Scientific Computing (100) Apply Scientific Computing filter
- Viral Tools (14) Apply Viral Tools filter
- Vivarium (7) Apply Vivarium filter
Publication Date
- 2026 (17) Apply 2026 filter
- 2025 (225) Apply 2025 filter
- 2024 (211) Apply 2024 filter
- 2023 (157) Apply 2023 filter
- 2022 (166) Apply 2022 filter
- 2021 (175) Apply 2021 filter
- 2020 (177) Apply 2020 filter
- 2019 (177) Apply 2019 filter
- 2018 (206) Apply 2018 filter
- 2017 (186) Apply 2017 filter
- 2016 (191) Apply 2016 filter
- 2015 (195) Apply 2015 filter
- 2014 (190) Apply 2014 filter
- 2013 (136) Apply 2013 filter
- 2012 (112) Apply 2012 filter
- 2011 (98) Apply 2011 filter
- 2010 (61) Apply 2010 filter
- 2009 (56) Apply 2009 filter
- 2008 (40) Apply 2008 filter
- 2007 (21) Apply 2007 filter
- 2006 (3) Apply 2006 filter
2800 Janelia Publications
Showing 1261-1270 of 2800 resultsIn the perception of color, wavelengths of light reflected off objects are transformed into the derived quantities of brightness, saturation and hue. Neurons responding selectively to hue have been reported in primate cortex, but it is unknown how their narrow tuning in color space is produced by upstream circuit mechanisms. We report the discovery of neurons in the Drosophila optic lobe with hue-selective properties, which enables circuit-level analysis of color processing. From our analysis of an electron microscopy volume of a whole Drosophila brain, we construct a connectomics-constrained circuit model that accounts for this hue selectivity. Our model predicts that recurrent connections in the circuit are critical for generating hue selectivity. Experiments using genetic manipulations to perturb recurrence in adult flies confirm this prediction. Our findings reveal a circuit basis for hue selectivity in color vision.
Physiological need states direct decision-making toward re-establishing homeostasis. Using a two-alternative forced choice task for mice that models elements of human decisions, we found that varying hunger and thirst states caused need-inappropriate choices, such as food seeking when thirsty. These results show limits on interoceptive knowledge of hunger and thirst states to guide decision-making. Instead, need states were identified after food and water consumption by outcome evaluation, which depended on the medial prefrontal cortex.
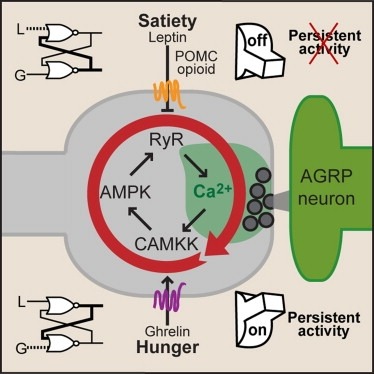
Synaptic plasticity in response to changes in physiologic state is coordinated by hormonal signals across multiple neuronal cell types. Here, we combine cell-type-specific electrophysiological, pharmacological, and optogenetic techniques to dissect neural circuits and molecular pathways controlling synaptic plasticity onto AGRP neurons, a population that regulates feeding. We find that food deprivation elevates excitatory synaptic input, which is mediated by a presynaptic positive feedback loop involving AMP-activated protein kinase. Potentiation of glutamate release was triggered by the orexigenic hormone ghrelin and exhibited hysteresis, persisting for hours after ghrelin removal. Persistent activity was reversed by the anorexigenic hormone leptin, and optogenetic photostimulation demonstrated involvement of opioid release from POMC neurons. Based on these experiments, we propose a memory storage device for physiological state constructed from bistable synapses that are flipped between two sustained activity states by transient exposure to hormones signaling energy levels.
Specificity remains a major challenge to current therapeutic strategies for cancer. Mutation associated neoantigens (MANAs) are products of genetic alterations, making them highly specific therapeutic targets. MANAs are HLA-presented (pHLA) peptides derived from intracellular mutant proteins that are otherwise inaccessible to antibody-based therapeutics. Here, we describe the cryo-EM structure of an antibody-MANA pHLA complex. Specifically, we determine a TCR mimic (TCRm) antibody bound to its MANA target, the KRAS peptide presented by HLA-A*03:01. Hydrophobic residues appear to account for the specificity of the mutant G12V residue. We also determine the structure of the wild-type G12 peptide bound to HLA-A*03:01, using X-ray crystallography. Based on these structures, we perform screens to validate the key residues required for peptide specificity. These experiments led us to a model for discrimination between the mutant and the wild-type peptides presented on HLA-A*03:01 based exclusively on hydrophobic interactions.
Neural processes that direct an animal’s actions toward environmental goals are critical elements for understanding behavior. The hypothalamus is closely associated with motivated behaviors required for survival and reproduction. Intense feeding, drinking, aggressive, and sexual behaviors can be produced by a simple neuronal stimulus applied to discrete hypothalamic regions. What can these "evoked behaviors" teach us about the neural processes that determine behavioral intent and intensity? Small populations of neurons sufficient to evoke a complex motivated behavior may be used as entry points to identify circuits that energize and direct behavior to specific goals. Here, I review recent applications of molecular genetic, optogenetic, and pharmacogenetic approaches that overcome previous limitations for analyzing anatomically complex hypothalamic circuits and their interactions with the rest of the brain. These new tools have the potential to bridge the gaps between neurobiological and psychological thinking about the mechanisms of complex motivated behavior.
One of the challenges in modern fluorescence microscopy is to reconcile the conventional utilization of microscopes as exploratory instruments with their emerging and rapidly expanding role as a quantitative tools. The contribution of microscopy to observational biology will remain enormous owing to the improvements in acquisition speed, imaging depth, resolution and biocompatibility of modern imaging instruments. However, the use of fluorescence microscopy to facilitate the quantitative measurements necessary to challenge hypotheses is a relatively recent concept, made possible by advanced optics, functional imaging probes and rapidly increasing computational power. We argue here that to fully leverage the rapidly evolving application of microscopes in hypothesis-driven biology, we not only need to ensure that images are acquired quantitatively but must also re-evaluate how microscopy-based experiments are designed. In this Opinion, we present a reverse logic that guides the design of quantitative fluorescence microscopy experiments. This unique approach starts from identifying the results that would quantitatively inform the hypothesis and map the process backward to microscope selection. This ensures that the quantitative aspects of testing the hypothesis remain the central focus of the entire experimental design.
We developed a significantly improved genetically encoded quantitative adenosine triphosphate (ATP) sensor to provide real-time dynamics of ATP levels in subcellular compartments. iATPSnFR2 is a variant of iATPSnFR1, a previously developed sensor that has circularly permuted super-folder GFP inserted between the ATP-binding helices of the ε-subunit of a bacterial F0-F1 ATPase. Optimizing the linkers joining the two domains resulted in a ∼ 5-6 fold improvement in the dynamic range compared to the previous generation sensor, with excellent discrimination against other analytes and affinity variants varying from 4 μM to 500 μM. A chimeric version of this sensor fused to either the HaloTag protein or a suitably spectrally separated fluorescent protein, provides a ratiometric readout allowing comparisons of ATP across cellular regions. Subcellular targeting of the sensor to nerve terminals reveals previously uncharacterized single synapse metabolic signatures, while targeting to the mitochondrial matrix allowed direct quantitative probing of oxidative phosphorylation dynamics.
Unprecedented technological advances in single-cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) technology have now made it possible to profile genome-wide expression in single cells at low cost and high throughput. There is substantial ongoing effort to use scRNA-seq measurements to identify the "cell types" that form components of a complex tissue, akin to taxonomizing species in ecology. Cell type classification from scRNA-seq data involves the application of computational tools rooted in dimensionality reduction and clustering, and statistical analysis to identify molecular signatures that are unique to each type. As datasets continue to grow in size and complexity, computational challenges abound, requiring analytical methods to be scalable, flexible, and robust. Moreover, careful consideration needs to be paid to experimental biases and statistical challenges that are unique to these measurements to avoid artifacts. This chapter introduces these topics in the context of cell-type identification, and outlines an instructive step-by-step example bioinformatic pipeline for researchers entering this field.
Bacterial small non-coding RNAs (sRNAs) are being recognized as novel widespread regulators of gene expression in response to environmental signals. Here, we present the first search for sRNA-encoding genes in the nitrogen-fixing endosymbiont Sinorhizobium meliloti, performed by a genome-wide computational analysis of its intergenic regions. Comparative sequence data from eight related alpha-proteobacteria were obtained, and the interspecies pairwise alignments were scored with the programs eQRNA and RNAz as complementary predictive tools to identify conserved and stable secondary structures corresponding to putative non-coding RNAs. Northern experiments confirmed that eight of the predicted loci, selected among the original 32 candidates as most probable sRNA genes, expressed small transcripts. This result supports the combined use of eQRNA and RNAz as a robust strategy to identify novel sRNAs in bacteria. Furthermore, seven of the transcripts accumulated differentially in free-living and symbiotic conditions. Experimental mapping of the 5’-ends of the detected transcripts revealed that their encoding genes are organized in autonomous transcription units with recognizable promoter and, in most cases, termination signatures. These findings suggest novel regulatory functions for sRNAs related to the interactions of alpha-proteobacteria with their eukaryotic hosts.