Filter
Result Type
- Apply filter
- Apply filter
- Apply filter
- Apply filter
- Apply filter
- Apply filter
- Apply filter
- Apply filter
- Apply filter
- Area Landing Page (8) Apply Area Landing Page filter
- Collaborations (2) Apply Collaborations filter
- Conferences (241) Apply Conferences filter
- Janelia Archives (19) Apply Janelia Archives filter
- Janelia Archives Landing (1) Apply Janelia Archives Landing filter
- Lab (59) Apply Lab filter
- News Stories (270) Apply News Stories filter
- Other (543) Apply Other filter
- People (648) Apply People filter
- Project Team (15) Apply Project Team filter
- Publications (2647) Apply Publications filter
- Support Team (21) Apply Support Team filter
- Theory Fellow Landing Page (4) Apply Theory Fellow Landing Page filter
- Tool (127) Apply Tool filter
Associated Lab
- Aguilera Castrejon Lab (6) Apply Aguilera Castrejon Lab filter
- Ahrens Lab (72) Apply Ahrens Lab filter
- Aso Lab (48) Apply Aso Lab filter
- Baker Lab (20) Apply Baker Lab filter
- Betzig Lab (111) Apply Betzig Lab filter
- Beyene Lab (14) Apply Beyene Lab filter
- Bock Lab (15) Apply Bock Lab filter
- Branson Lab (59) Apply Branson Lab filter
- Card Lab (35) Apply Card Lab filter
- Cardona Lab (44) Apply Cardona Lab filter
- Chklovskii Lab (10) Apply Chklovskii Lab filter
- Clapham Lab (23) Apply Clapham Lab filter
- Cui Lab (20) Apply Cui Lab filter
- Darshan Lab (8) Apply Darshan Lab filter
- Dennis Lab (7) Apply Dennis Lab filter
- Dickson Lab (34) Apply Dickson Lab filter
- Druckmann Lab (21) Apply Druckmann Lab filter
- Dudman Lab (50) Apply Dudman Lab filter
- Eddy/Rivas Lab (30) Apply Eddy/Rivas Lab filter
- Egnor Lab (5) Apply Egnor Lab filter
- Espinosa Medina Lab (25) Apply Espinosa Medina Lab filter
- Feliciano Lab (14) Apply Feliciano Lab filter
- Fetter Lab (31) Apply Fetter Lab filter
- Fitzgerald Lab (16) Apply Fitzgerald Lab filter
- Freeman Lab (16) Apply Freeman Lab filter
- Funke Lab (45) Apply Funke Lab filter
- Gonen Lab (60) Apply Gonen Lab filter
- Grigorieff Lab (34) Apply Grigorieff Lab filter
- Harris Lab (62) Apply Harris Lab filter
- Heberlein Lab (15) Apply Heberlein Lab filter
- Hermundstad Lab (30) Apply Hermundstad Lab filter
- Hess Lab (84) Apply Hess Lab filter
- Ilanges Lab (9) Apply Ilanges Lab filter
- Jayaraman Lab (57) Apply Jayaraman Lab filter
- Ji Lab (34) Apply Ji Lab filter
- Johnson Lab (8) Apply Johnson Lab filter
- Kainmueller Lab (1) Apply Kainmueller Lab filter
- Karpova Lab (24) Apply Karpova Lab filter
- Keleman Lab (8) Apply Keleman Lab filter
- Keller Lab (81) Apply Keller Lab filter
- Koay Lab (8) Apply Koay Lab filter
- Lavis Lab (154) Apply Lavis Lab filter
- Lee (Albert) Lab (32) Apply Lee (Albert) Lab filter
- Leonardo Lab (19) Apply Leonardo Lab filter
- Li Lab (11) Apply Li Lab filter
- Lippincott-Schwartz Lab (108) Apply Lippincott-Schwartz Lab filter
- Liu (Yin) Lab (8) Apply Liu (Yin) Lab filter
- Liu (Zhe) Lab (64) Apply Liu (Zhe) Lab filter
- Looger Lab (143) Apply Looger Lab filter
- Magee Lab (31) Apply Magee Lab filter
- Menon Lab (12) Apply Menon Lab filter
- Murphy Lab (7) Apply Murphy Lab filter
- O'Shea Lab (12) Apply O'Shea Lab filter
- Otopalik Lab (9) Apply Otopalik Lab filter
- Pachitariu Lab (42) Apply Pachitariu Lab filter
- Pastalkova Lab (6) Apply Pastalkova Lab filter
- Pavlopoulos Lab (7) Apply Pavlopoulos Lab filter
- Pedram Lab (12) Apply Pedram Lab filter
- Podgorski Lab (19) Apply Podgorski Lab filter
- Reiser Lab (62) Apply Reiser Lab filter
- Riddiford Lab (21) Apply Riddiford Lab filter
- Romani Lab (45) Apply Romani Lab filter
- Rubin Lab (123) Apply Rubin Lab filter
- Ryan Lab (1) Apply Ryan Lab filter
- Saalfeld Lab (57) Apply Saalfeld Lab filter
- Satou Lab (8) Apply Satou Lab filter
- Scheffer Lab (39) Apply Scheffer Lab filter
- Schreiter Lab (62) Apply Schreiter Lab filter
- Sgro Lab (10) Apply Sgro Lab filter
- Shroff Lab (43) Apply Shroff Lab filter
- Simpson Lab (18) Apply Simpson Lab filter
- Singer Lab (39) Apply Singer Lab filter
- Spruston Lab (75) Apply Spruston Lab filter
- Stern Lab (83) Apply Stern Lab filter
- Sternson Lab (52) Apply Sternson Lab filter
- Stringer Lab (37) Apply Stringer Lab filter
- Svoboda Lab (145) Apply Svoboda Lab filter
- Tebo Lab (20) Apply Tebo Lab filter
- Tervo Lab (14) Apply Tervo Lab filter
- Tillberg Lab (22) Apply Tillberg Lab filter
- Tjian Lab (19) Apply Tjian Lab filter
- Truman Lab (59) Apply Truman Lab filter
- Turaga Lab (52) Apply Turaga Lab filter
- Turner Lab (33) Apply Turner Lab filter
- Vale Lab (13) Apply Vale Lab filter
- Voigts Lab (9) Apply Voigts Lab filter
- Wang (Meng) Lab (31) Apply Wang (Meng) Lab filter
- Wang (Shaohe) Lab (11) Apply Wang (Shaohe) Lab filter
- Wong-Campos Lab (4) Apply Wong-Campos Lab filter
- Wu Lab (9) Apply Wu Lab filter
- Zlatic Lab (26) Apply Zlatic Lab filter
- Zuker Lab (5) Apply Zuker Lab filter
Associated Project Team
- CellMap (39) Apply CellMap filter
- COSEM (3) Apply COSEM filter
- FIB-SEM Technology (8) Apply FIB-SEM Technology filter
- Fly Descending Interneuron (12) Apply Fly Descending Interneuron filter
- Fly Functional Connectome (15) Apply Fly Functional Connectome filter
- Fly Olympiad (5) Apply Fly Olympiad filter
- FlyEM (64) Apply FlyEM filter
- FlyLight (58) Apply FlyLight filter
- GENIE (67) Apply GENIE filter
- Integrative Imaging (2) Apply Integrative Imaging filter
- Larval Olympiad (2) Apply Larval Olympiad filter
- MouseLight (26) Apply MouseLight filter
- NeuroSeq (2) Apply NeuroSeq filter
- ThalamoSeq (1) Apply ThalamoSeq filter
- Tool Translation Team (T3) (36) Apply Tool Translation Team (T3) filter
- Transcription Imaging (48) Apply Transcription Imaging filter
Associated Support Team
- Project Pipeline Support (14) Apply Project Pipeline Support filter
- Anatomy and Histology (24) Apply Anatomy and Histology filter
- Cryo-Electron Microscopy (41) Apply Cryo-Electron Microscopy filter
- Electron Microscopy (21) Apply Electron Microscopy filter
- Flow Cytometry (4) Apply Flow Cytometry filter
- Gene Targeting and Transgenics (19) Apply Gene Targeting and Transgenics filter
- Immortalized Cell Line Culture (6) Apply Immortalized Cell Line Culture filter
- Integrative Imaging (32) Apply Integrative Imaging filter
- Invertebrate Shared Resource (50) Apply Invertebrate Shared Resource filter
- Janelia Experimental Technology (103) Apply Janelia Experimental Technology filter
- Management Team (1) Apply Management Team filter
- Mass Spectrometry (4) Apply Mass Spectrometry filter
- Media Facil\ (6) Apply Media Facil\ filter
- Molecular Genomics (22) Apply Molecular Genomics filter
- Primary & iPS Cell Culture (24) Apply Primary & iPS Cell Culture filter
- Project Technical Resources (61) Apply Project Technical Resources filter
- Quantitative Genomics (26) Apply Quantitative Genomics filter
- Scientific Computing Software (128) Apply Scientific Computing Software filter
- Scientific Computing Systems (13) Apply Scientific Computing Systems filter
- Viral Tools (22) Apply Viral Tools filter
- Vivarium (10) Apply Vivarium filter
Publication Date
- 2025 (85) Apply 2025 filter
- 2024 (252) Apply 2024 filter
- 2023 (192) Apply 2023 filter
- 2022 (193) Apply 2022 filter
- 2021 (187) Apply 2021 filter
- 2020 (194) Apply 2020 filter
- 2019 (201) Apply 2019 filter
- 2018 (221) Apply 2018 filter
- 2017 (202) Apply 2017 filter
- 2016 (207) Apply 2016 filter
- 2015 (222) Apply 2015 filter
- 2014 (216) Apply 2014 filter
- 2013 (152) Apply 2013 filter
- 2012 (112) Apply 2012 filter
- 2011 (98) Apply 2011 filter
- 2010 (61) Apply 2010 filter
- 2009 (56) Apply 2009 filter
- 2008 (40) Apply 2008 filter
- 2007 (21) Apply 2007 filter
- 2006 (3) Apply 2006 filter
Tool Types
- Data (9) Apply Data filter
- Data Application (7) Apply Data Application filter
- Figshare (1) Apply Figshare filter
- Human Health (2) Apply Human Health filter
- Imaging Instrumentation (11) Apply Imaging Instrumentation filter
- Laboratory Hardware (3) Apply Laboratory Hardware filter
- Laboratory Tool (6) Apply Laboratory Tool filter
- Laboratory Tools (51) Apply Laboratory Tools filter
- Medical Technology (1) Apply Medical Technology filter
- Model Organisms (9) Apply Model Organisms filter
- Reagents (24) Apply Reagents filter
- Software (20) Apply Software filter
4761 Results
Showing 41-50 of 4761 resultsObject detection and classification are key tasks in computer vision that can facilitate high-throughput image analysis of microscopy data. We present a set of local image descriptors for three-dimensional (3D) microscopy datasets inspired by the well-known Haar wavelet framework. We add orientation, illumination and scale information by assuming that the neighborhood surrounding points of interests in the image can be described with ellipsoids, and we increase discriminative power by incorporating edge and shape information into the features. The calculation of the local image descriptors is implemented in a Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) in order to reduce computation time to 1 millisecond per object of interest. We present results for cell division detection in 3D time-lapse fluorescence microscopy with 97.6% accuracy.
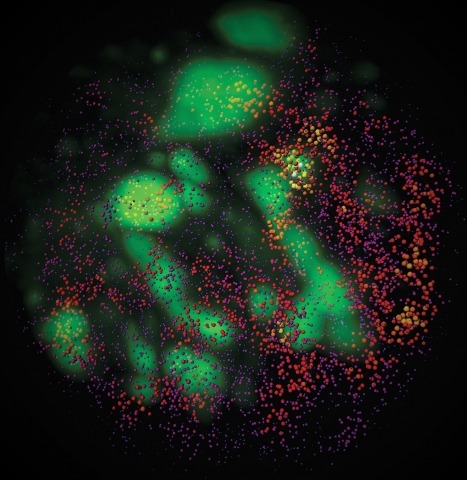
Combinatorial cis-regulatory networks encoded in animal genomes represent the foundational gene expression mechanism for directing cell-fate commitment and maintenance of cell identity by transcription factors (TFs). However, the 3D spatial organization of cis-elements and how such sub-nuclear structures influence TF activity remain poorly understood. Here, we combine lattice light-sheet imaging, single-molecule tracking, numerical simulations, and ChIP-exo mapping to localize and functionally probe Sox2 enhancer-organization in living embryonic stem cells. Sox2 enhancers form 3D-clusters that are segregated from heterochromatin but overlap with a subset of Pol II enriched regions. Sox2 searches for specific binding targets via a 3D-diffusion dominant mode when shuttling long-distances between clusters while chromatin-bound states predominate within individual clusters. Thus, enhancer clustering may reduce global search efficiency but enables rapid local fine-tuning of TF search parameters. Our results suggest an integrated model linking cis-element 3D spatial distribution to local-versus-global target search modalities essential for regulating eukaryotic gene transcription.
3D live imaging is important for a better understanding of biological processes, but it is challenging with current techniques such as spinning-disk confocal microscopy. Bessel beam plane illumination microscopy allows high-speed 3D live fluorescence imaging of living cellular and multicellular specimens with nearly isotropic spatial resolution, low photobleaching and low photodamage. Unlike conventional fluorescence imaging techniques that usually have a unique operation mode, Bessel plane illumination has several modes that offer different performance with different imaging metrics. To achieve optimal results from this technique, the appropriate operation mode needs to be selected and the experimental setting must be optimized for the specific application and associated sample properties. Here we explain the fundamental working principles of this technique, discuss the pros and cons of each operational mode and show through examples how to optimize experimental parameters. We also describe the procedures needed to construct, align and operate a Bessel beam plane illumination microscope by using our previously reported system as an example, and we list the necessary equipment to build such a microscope. Assuming all components are readily available, it would take a person skilled in optical instrumentation \~{}1 month to assemble and operate a microscope according to this protocol.
A major frontier in single cell biology is decoding how transcriptional states result in cellular-level architectural changes, ultimately driving function. A remarkable example of this cellular remodelling program is the differentiation of airway stem cells into the human respiratory multiciliated epithelium, a tissue barrier protecting against bacteria, viruses and particulate matter. Here, we present the first isotropic three-dimensional map of the airway epithelium at the nanometre scale unveiling the coordinated changes in cellular organisation, organelle topology and contacts, occurring during multiciliogenesis. This analysis led us to discover a cellular mechanism of communication whereby motile cilia relay mechanical information to mitochondria through striated cytoskeletal fibres, the rootlets, to promote effective ciliary motility and ATP generation. Altogether, this study integrates nanometre-scale structural, functional and dynamic insights to elucidate fundamental mechanisms responsible for airway defence.
New methods in stem cell 3D organoid tissue culture, advanced imaging and big data image analytics now allow tissue scale 4D cell biology, but currently available analytical pipelines are inadequate for handing and analyzing the resulting gigabytes and terabytes of high-content imaging data. We expressed fluorescent protein fusions of clathrin and dynamin2 at endogenous levels in genome-edited human embryonic stem cells, which were differentiated into hESC-derived intestinal epithelial organoids. Lattice Light-Sheet Imaging with adaptive optics (AO-LLSM) allowed us to image large volumes of these organoids (70µm x 60µm x 40µm xyz) at 5.7s/frame. We developed an open source data analysis package termed pyLattice to process the resulting large (∼60Gb) movie datasets and to track clathrin-mediated endocytosis (CME) events. CME tracks could be recorded from ∼35 cells at a time, resulting in ∼4000 processed tracks per movie. Based on their localization in the organoid, we classified CME tracks into apical, lateral and basal events and found that CME dynamics are similar for all three classes, despite reported differences in membrane tension. pyLattice coupled with AO-LLSM makes possible quantitative, high temporal and spatial resolution analysis of subcellular events within tissues. Movie S1 Movie S1 Thresholded 3D AO-LLSM data of an intestinal epithelial organoid showing clathrin (red) and dynamin2 (green) puncta in surface depiction. The movie zooms out from a single clathrin mediated endocytosis event that shows both clathrin and dynamin2 at the same location to eventually show the whole AO-LLSM field of view. Nuclear envelopes and the outer membranes of the tissue are depicted in transparent white. Movie S2 Movie S2 Thresholded 3D AO-LLSM data of an intestinal epithelial organoid showing clathrin (red) and dynamin2 (green) puncta in surface depiction. The movie rotates the AO-LLSM field of view. Nuclear envelopes and the outer membranes of the tissue are depicted in transparent white. Movie S3 Movie S3 Thresholded 3D AO-LLSM data of an intestinal epithelial organoid. The curved surface is of the spherical organoid is visible as the movie rotates. Clathrin puncta are visible throughout the tissue (white). Movie S4 Movie S4 The detection step in the data processing pipeline retrieves all clathrin puncta in the volume. Detected puncta are marked with a cube (blue). Movie S5 Movie S5 Zoom on one clathrin puncta in the thresholded 3D dataset. The punctum of interest is marked with a blue cube. Other puncta are also visible. Movie S6 Movie S6 Zoom on the same clathrin puncta as in M3 in non-thresholded 3D data. The surrounding fluorescence is visible as a transparent cloud.