Filter
Associated Lab
- Aso Lab (30) Apply Aso Lab filter
- Betzig Lab (1) Apply Betzig Lab filter
- Bock Lab (2) Apply Bock Lab filter
- Branson Lab (9) Apply Branson Lab filter
- Card Lab (5) Apply Card Lab filter
- Clapham Lab (1) Apply Clapham Lab filter
- Dickson Lab (2) Apply Dickson Lab filter
- Druckmann Lab (1) Apply Druckmann Lab filter
- Fetter Lab (1) Apply Fetter Lab filter
- Funke Lab (2) Apply Funke Lab filter
- Harris Lab (3) Apply Harris Lab filter
- Heberlein Lab (2) Apply Heberlein Lab filter
- Hermundstad Lab (2) Apply Hermundstad Lab filter
- Hess Lab (6) Apply Hess Lab filter
- Jayaraman Lab (7) Apply Jayaraman Lab filter
- Lippincott-Schwartz Lab (1) Apply Lippincott-Schwartz Lab filter
- Looger Lab (2) Apply Looger Lab filter
- O'Shea Lab (1) Apply O'Shea Lab filter
- Otopalik Lab (1) Apply Otopalik Lab filter
- Reiser Lab (16) Apply Reiser Lab filter
- Riddiford Lab (1) Apply Riddiford Lab filter
- Romani Lab (2) Apply Romani Lab filter
- Rubin Lab (146) Apply Rubin Lab filter
- Saalfeld Lab (5) Apply Saalfeld Lab filter
- Scheffer Lab (8) Apply Scheffer Lab filter
- Schreiter Lab (1) Apply Schreiter Lab filter
- Simpson Lab (3) Apply Simpson Lab filter
- Singer Lab (1) Apply Singer Lab filter
- Spruston Lab (1) Apply Spruston Lab filter
- Stern Lab (1) Apply Stern Lab filter
- Svoboda Lab (3) Apply Svoboda Lab filter
- Tjian Lab (1) Apply Tjian Lab filter
- Truman Lab (4) Apply Truman Lab filter
- Turaga Lab (1) Apply Turaga Lab filter
- Turner Lab (5) Apply Turner Lab filter
- Zuker Lab (1) Apply Zuker Lab filter
Associated Project Team
- CellMap (1) Apply CellMap filter
- Fly Functional Connectome (4) Apply Fly Functional Connectome filter
- Fly Olympiad (3) Apply Fly Olympiad filter
- FlyEM (12) Apply FlyEM filter
- FlyLight (20) Apply FlyLight filter
- GENIE (1) Apply GENIE filter
- Transcription Imaging (1) Apply Transcription Imaging filter
Publication Date
- 2025 (7) Apply 2025 filter
- 2024 (4) Apply 2024 filter
- 2023 (5) Apply 2023 filter
- 2022 (1) Apply 2022 filter
- 2021 (4) Apply 2021 filter
- 2020 (9) Apply 2020 filter
- 2019 (6) Apply 2019 filter
- 2018 (7) Apply 2018 filter
- 2017 (15) Apply 2017 filter
- 2016 (3) Apply 2016 filter
- 2015 (16) Apply 2015 filter
- 2014 (9) Apply 2014 filter
- 2013 (5) Apply 2013 filter
- 2012 (8) Apply 2012 filter
- 2011 (4) Apply 2011 filter
- 2010 (4) Apply 2010 filter
- 2009 (2) Apply 2009 filter
- 2008 (4) Apply 2008 filter
- 2007 (2) Apply 2007 filter
- 2006 (1) Apply 2006 filter
- 2002 (1) Apply 2002 filter
- 2000 (2) Apply 2000 filter
- 1999 (1) Apply 1999 filter
- 1997 (1) Apply 1997 filter
- 1995 (2) Apply 1995 filter
- 1994 (2) Apply 1994 filter
- 1993 (2) Apply 1993 filter
- 1992 (1) Apply 1992 filter
- 1991 (2) Apply 1991 filter
- 1990 (3) Apply 1990 filter
- 1989 (2) Apply 1989 filter
- 1987 (2) Apply 1987 filter
- 1986 (1) Apply 1986 filter
- 1985 (1) Apply 1985 filter
- 1984 (1) Apply 1984 filter
- 1983 (1) Apply 1983 filter
- 1982 (2) Apply 1982 filter
- 1981 (1) Apply 1981 filter
- 1979 (1) Apply 1979 filter
- 1973 (1) Apply 1973 filter
Type of Publication
146 Publications
Showing 91-100 of 146 resultsHow memories of past events influence behavior is a key question in neuroscience. The major associative learning center in Drosophila, the Mushroom Body (MB), communicates to the rest of the brain through Mushroom Body Output Neurons (MBONs). While 21 MBON cell types have their dendrites confined to small compartments of the MB lobes, analysis of EM connectomes revealed the presence of an additional 14 MBON cell types that are atypical in having dendritic input both within the MB lobes and in adjacent brain regions. Genetic reagents for manipulating atypical MBONs and experimental data on their functions has been lacking. In this report we describe new cell-type-specific GAL4 drivers for many MBONs, including the majority of atypical MBONs. Using these genetic reagents, we conducted optogenetic activation screening to examine their ability to drive behaviors and learning. These reagents provide important new tools for the study of complex behaviors in Drosophila.
Animals employ diverse learning rules and synaptic plasticity dynamics to record temporal and statistical information about the world. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying this diversity are poorly understood. The anatomically defined compartments of the insect mushroom body function as parallel units of associative learning, with different learning rates, memory decay dynamics and flexibility (Aso & Rubin 2016). Here we show that nitric oxide (NO) acts as a neurotransmitter in a subset of dopaminergic neurons in . NO's effects develop more slowly than those of dopamine and depend on soluble guanylate cyclase in postsynaptic Kenyon cells. NO acts antagonistically to dopamine; it shortens memory retention and facilitates the rapid updating of memories. The interplay of NO and dopamine enables memories stored in local domains along Kenyon cell axons to be specialized for predicting the value of odors based only on recent events. Our results provide key mechanistic insights into how diverse memory dynamics are established in parallel memory systems.
The insect mushroom body (MB) is a conserved brain structure that plays key roles in a diverse array of behaviors. The MB is the primary invertebrate model of neural circuits related to memory formation and storage, and its development, morphology, wiring, and function has been extensively studied. MBs consist of intrinsic Kenyon Cells that are divided into three major neuron classes (γ, α'/β' and α/β) and 7 cell subtypes (γd, γm, α'/β'ap, α'/β'm, α/βp, α/βs and α/βc) based on their birth order, morphology, and connectivity. These subtypes play distinct roles in memory processing, however the underlying transcriptional differences are unknown. Here, we used RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) to profile the nuclear transcriptomes of each MB neuronal cell subtypes. We identified 350 MB class- or subtype-specific genes, including the widely used α/β class marker and the α'/β' class marker Immunostaining corroborates the RNA-seq measurements at the protein level for several cases. Importantly, our data provide a full accounting of the neurotransmitter receptors, transporters, neurotransmitter biosynthetic enzymes, neuropeptides, and neuropeptide receptors expressed within each of these cell types. This high-quality, cell type-level transcriptome catalog for the MB provides a valuable resource for the fly neuroscience community.
We describe the development and application of methods for high-throughput neuroanatomy in Drosophila using light microscopy. These tools enable efficient multicolor stochastic labeling of neurons at both low and high densities. Expression of multiple membrane-targeted and distinct epitope-tagged proteins is controlled both by a transcriptional driver and by stochastic, recombinase-mediated excision of transcription-terminating cassettes. This MultiColor FlpOut (MCFO) approach can be used to reveal cell shapes and relative cell positions and to track the progeny of precursor cells through development. Using two different recombinases, the number of cells labeled and the number of color combinations observed in those cells can be controlled separately. We demonstrate the utility of MCFO in a detailed study of diversity and variability of Distal medulla (Dm) neurons, multicolumnar local interneurons in the adult visual system. Similar to many brain regions, the medulla has a repetitive columnar structure that supports parallel information processing together with orthogonal layers of cell processes that enable communication between columns. We find that, within a medulla layer, processes of the cells of a given Dm neuron type form distinct patterns that reflect both the morphology of individual cells and the relative positions of their arbors. These stereotyped cell arrangements differ between cell types and can even differ for the processes of the same cell type in different medulla layers. This unexpected diversity of coverage patterns provides multiple independent ways of integrating visual information across the retinotopic columns and implies the existence of multiple developmental mechanisms that generate these distinct patterns.
The visual system of Drosophila is an excellent model for determining the interactions that direct the differentiation of the nervous system’s many unique cell types. Glia are essential not only in the development of the nervous system, but also in the function of those neurons with which they become associated in the adult. Given their role in visual system development and adult function we need to both accurately and reliably identify the different subtypes of glia, and to relate the glial subtypes in the larval brain to those previously described for the adult. We viewed driver expression in subsets of larval eye disc glia through the earliest stages of pupal development to reveal the counterparts of these cells in the adult. Two populations of glia exist in the lamina, the first neuropil of the adult optic lobe: those that arise from precursors in the eye-disc/optic stalk and those that arise from precursors in the brain. In both cases, a single larval source gives rise to at least three different types of adult glia. Furthermore, analysis of glial cell types in the second neuropil, the medulla, has identified at least four types of astrocyte-like (reticular) glia. Our clarification of the lamina’s adult glia and identification of their larval origins, particularly the respective eye disc and larval brain contributions, begin to define developmental interactions which establish the different subtypes of glia.
How brains are hardwired to produce aggressive behavior, and how aggression circuits are related to those that mediate courtship, is not well understood. A large-scale screen for aggression-promoting neurons in Drosophila identified several independent hits that enhanced both inter-male aggression and courtship. Genetic intersections revealed that 8-10 P1 interneurons, previously thought to exclusively control male courtship, were sufficient to promote fighting. Optogenetic experiments indicated that P1 activation could promote aggression at a threshold below that required for wing extension. P1 activation in the absence of wing extension triggered persistent aggression via an internal state that could endure for minutes. High-frequency P1 activation promoted wing extension and suppressed aggression during photostimulation, whereas aggression resumed and wing extension was inhibited following photostimulation offset. Thus, P1 neuron activation promotes a latent, internal state that facilitates aggression and courtship, and controls the overt expression of these social behaviors in a threshold-dependent, inverse manner.
Although all sensory circuits ascend to higher brain areas where stimuli are represented in sparse, stimulus-specific activity patterns, relatively little is known about sensory coding on the descending side of neural circuits, as a network converges. In insects, mushroom bodies have been an important model system for studying sparse coding in the olfactory system, where this format is important for accurate memory formation. In Drosophila, it has recently been shown that the 2,000 Kenyon cells of the mushroom body converge onto a population of only 34 mushroom body output neurons (MBONs), which fall into 21 anatomically distinct cell types. Here we provide the first, to our knowledge, comprehensive view of olfactory representations at the fourth layer of the circuit, where we find a clear transition in the principles of sensory coding. We show that MBON tuning curves are highly correlated with one another. This is in sharp contrast to the process of progressive decorrelation of tuning in the earlier layers of the circuit. Instead, at the population level, odour representations are reformatted so that positive and negative correlations arise between representations of different odours. At the single-cell level, we show that uniquely identifiable MBONs display profoundly different tuning across different animals, but that tuning of the same neuron across the two hemispheres of an individual fly was nearly identical. Thus, individualized coordination of tuning arises at this level of the olfactory circuit. Furthermore, we find that this individualization is an active process that requires a learning-related gene, rutabaga. Ultimately, neural circuits have to flexibly map highly stimulus-specific information in sparse layers onto a limited number of different motor outputs. The reformatting of sensory representations we observe here may mark the beginning of this sensory-motor transition in the olfactory system.
The Drosophila mushroom body (MB) is a key associative memory center that has also been implicated in the control of sleep. However, the identity of MB neurons underlying homeostatic sleep regulation, as well as the types of sleep signals generated by specific classes of MB neurons, has remained poorly understood. We recently identified two MB output neuron (MBON) classes whose axons convey sleep control signals from the MB to converge in the same downstream target region: a cholinergic sleep-promoting MBON class and a glutamatergic wake-promoting MBON class. Here, we deploy a combination of neurogenetic, behavioral, and physiological approaches to identify and mechanistically dissect sleep-controlling circuits of the MB. Our studies reveal the existence of two segregated excitatory synaptic microcircuits that propagate homeostatic sleep information from different populations of intrinsic MB "Kenyon cells" (KCs) to specific sleep-regulating MBONs: sleep-promoting KCs increase sleep by preferentially activating the cholinergic MBONs, while wake-promoting KCs decrease sleep by preferentially activating the glutamatergic MBONs. Importantly, activity of the sleep-promoting MB microcircuit is increased by sleep deprivation and is necessary for homeostatic rebound sleep (i.e., the increased sleep that occurs after, and in compensation for, sleep lost during deprivation). These studies reveal for the first time specific functional connections between subsets of KCs and particular MBONs and establish the identity of synaptic microcircuits underlying transmission of homeostatic sleep signals in the MB.
We have conducted a genetic screen for mutations that decrease the effectiveness of signaling by a protein tyrosine kinase, the product of the Drosophila melanogaster sevenless gene. These mutations define seven genes whose wild-type products may be required for signaling by sevenless. Four of the seven genes also appear to be essential for signaling by a second protein tyrosine kinase, the product of the Ellipse gene. The putative products of two of these seven genes have been identified. One encodes a ras protein. The other locus encodes a protein that is homologous to the S. cerevisiae CDC25 protein, an activator of guanine nucleotide exchange by ras proteins. These results suggest that the stimulation of ras protein activity is a key element in the signaling by sevenless and Ellipse and that this stimulation may be achieved by activating the exchange of GTP for bound GDP by the ras protein.
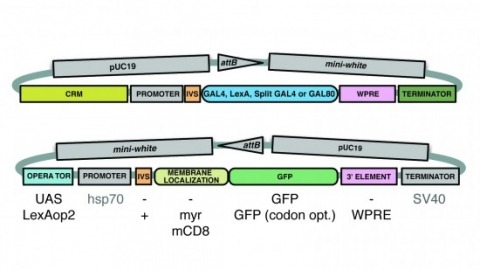
A wide variety of biological experiments rely on the ability to express an exogenous gene in a transgenic animal at a defined level and in a spatially and temporally controlled pattern. We describe major improvements of the methods available for achieving this objective in Drosophila melanogaster. We have systematically varied core promoters, UTRs, operator sequences, and transcriptional activating domains used to direct gene expression with the GAL4, LexA, and Split GAL4 transcription factors and the GAL80 transcriptional repressor. The use of site-specific integration allowed us to make quantitative comparisons between different constructs inserted at the same genomic location. We also characterized a set of PhiC31 integration sites for their ability to support transgene expression of both drivers and responders in the nervous system. The increased strength and reliability of these optimized reagents overcome many of the previous limitations of these methods and will facilitate genetic manipulations of greater complexity and sophistication.